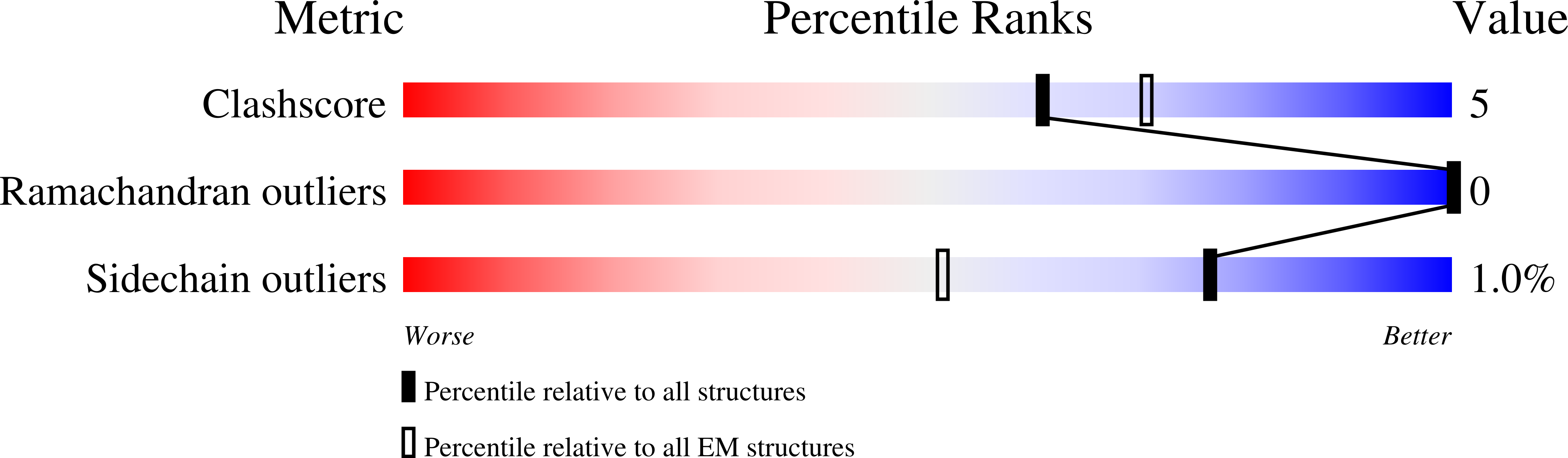Structural analyses of the PKA RII beta holoenzyme containing the oncogenic DnaJB1-PKAc fusion protein reveal protomer asymmetry and fusion-induced allosteric perturbations in fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma.
Lu, T.W., Aoto, P.C., Weng, J.H., Nielsen, C., Cash, J.N., Hall, J., Zhang, P., Simon, S.M., Cianfrocco, M.A., Taylor, S.S.(2020) PLoS Biol 18: e3001018-e3001018
- PubMed: 33370777
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3001018
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
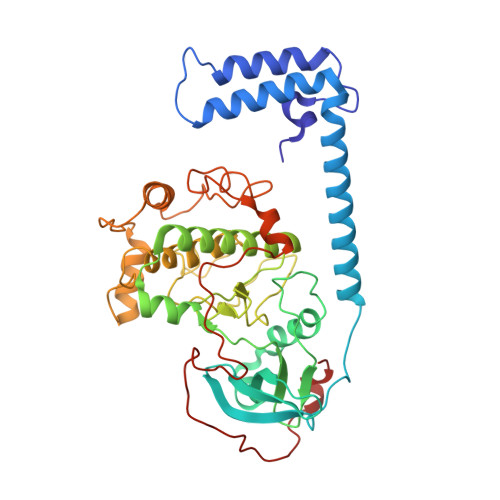
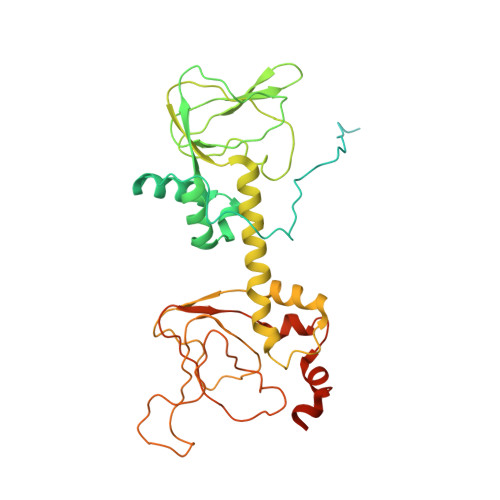
6WJF, 6WJG - PubMed Abstract:
When the J-domain of the heat shock protein DnaJB1 is fused to the catalytic (C) subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA), replacing exon 1, this fusion protein, J-C subunit (J-C), becomes the driver of fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma (FL-HCC). Here, we use cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to characterize J-C bound to RIIβ, the major PKA regulatory (R) subunit in liver, thus reporting the first cryo-EM structure of any PKA holoenzyme. We report several differences in both structure and dynamics that could not be captured by the conventional crystallography approaches used to obtain prior structures. Most striking is the asymmetry caused by the absence of the second cyclic nucleotide binding (CNB) domain and the J-domain in one of the RIIβ:J-C protomers. Using molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, we discovered that this asymmetry is already present in the wild-type (WT) RIIβ2C2 but had been masked in the previous crystal structure. This asymmetry may link to the intrinsic allosteric regulation of all PKA holoenzymes and could also explain why most disease mutations in PKA regulatory subunits are dominant negative. The cryo-EM structure, combined with small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), also allowed us to predict the general position of the Dimerization/Docking (D/D) domain, which is essential for localization and interacting with membrane-anchored A-Kinase-Anchoring Proteins (AKAPs). This position provides a multivalent mechanism for interaction of the RIIβ holoenzyme with membranes and would be perturbed in the oncogenic fusion protein. The J-domain also alters several biochemical properties of the RIIβ holoenzyme: It is easier to activate with cAMP, and the cooperativity is reduced. These results provide new insights into how the finely tuned allosteric PKA signaling network is disrupted by the oncogenic J-C subunit, ultimately leading to the development of FL-HCC.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, California, United States of America.