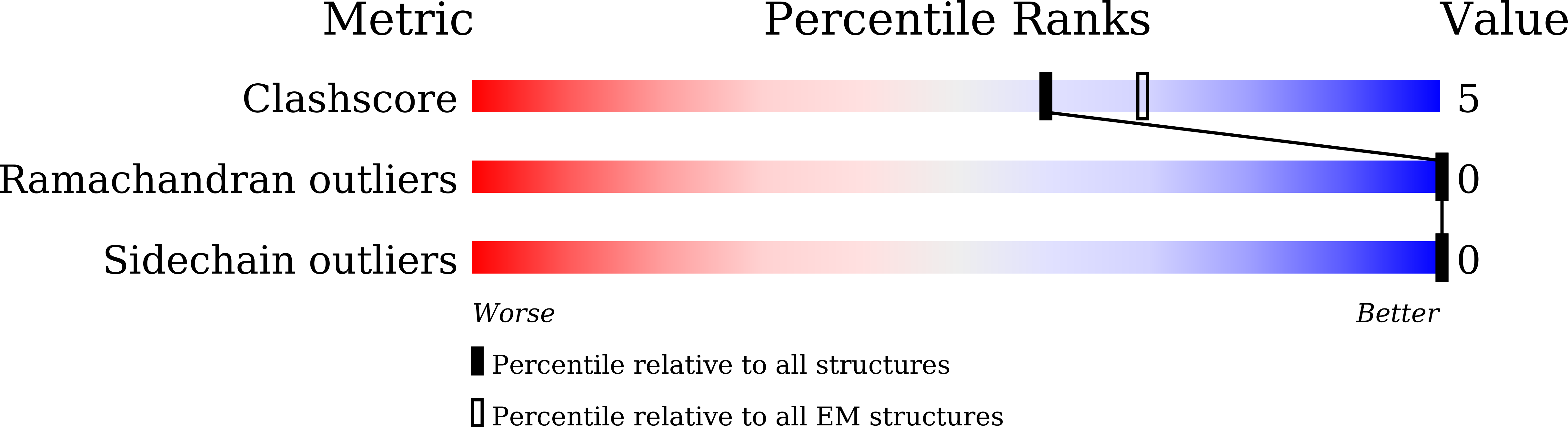Phosphorylation and O-GlcNAcylation at the same alpha-synuclein site generate distinct fibril structures.
Hu, J., Xia, W., Zeng, S., Lim, Y.J., Tao, Y., Sun, Y., Zhao, L., Wang, H., Le, W., Li, D., Zhang, S., Liu, C., Li, Y.M.(2024) Nat Commun 15: 2677-2677
- PubMed: 38538591
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46898-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8JEX, 8JEY - PubMed Abstract:
α-Synuclein forms amyloid fibrils that are critical in the progression of Parkinson's disease and serves as the pathological hallmark of this condition. Different posttranslational modifications have been identified at multiple sites of α-synuclein, influencing its conformation, aggregation and function. Here, we investigate how disease-related phosphorylation and O-GlcNAcylation at the same α-synuclein site (S87) affect fibril structure and neuropathology. Using semi-synthesis, we obtained homogenous α-synuclein monomer with site-specific phosphorylation (pS87) and O-GlcNAcylation (gS87) at S87, respectively. Cryo-EM revealed that pS87 and gS87 α-synuclein form two distinct fibril structures. The GlcNAc situated at S87 establishes interactions with K80 and E61, inducing a unique iron-like fold with the GlcNAc molecule on the iron handle. Phosphorylation at the same site prevents a lengthy C-terminal region including residues 73 to 140 from incorporating into the fibril core due to electrostatic repulsion. Instead, the N-terminal half of the fibril (1-72) takes on an arch-like fibril structure. We further show that both pS87 and gS87 α-synuclein fibrils display reduced neurotoxicity and propagation activity compared with unmodified α-synuclein fibrils. Our findings demonstrate that different posttranslational modifications at the same site can produce distinct fibril structures, which emphasizes link between posttranslational modifications and amyloid fibril formation and pathology.
Organizational Affiliation:
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology (Ministry of Education), Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084, China.