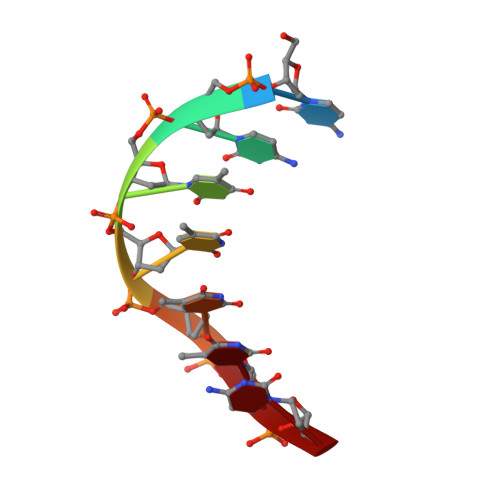
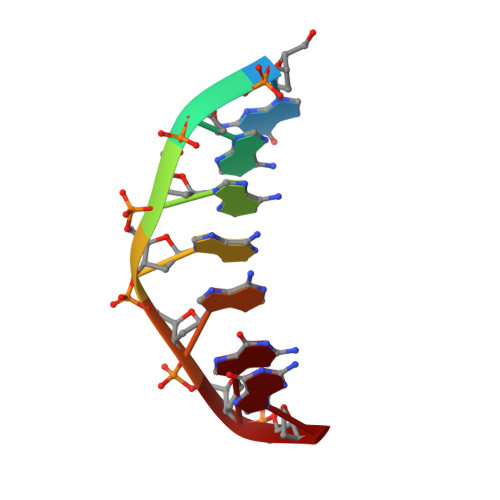
Solution structure of the covalent duocarmycin A-DNA duplex complex.
Lin, C.H., Patel, D.J.(1995) J Mol Biol 248: 162-179
- PubMed: 7731041
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1995.0209
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
107D - PubMed Abstract:
Duocarmycin A is an antitumour antibiotic that binds covalently to the minor groove N-3 position of adenine with sequence specificity for the 3'-adenine in a d(A-A-A-A) tract in duplex DNA. The adenine ring becomes protonated on duocarmycin adduct formation resulting in charge delocalization over the purine ring system. We report on the solution structure of duocarmycin A bound site specifically to A12 (designated *A12+) in the sequence context d(T3-T4-T5-T6).d(A9-A10-A11-*A12+) within a hairpin duplex. The solution structure was solved based on a combined NMR-molecular dynamics study including NOE based intensity refinement. The A and B-rings of duocarmycin are positioned deep within the walls of the minor groove with the B-ring (which is furthest from the covalent linkage site) directed towards the 5'-end of the modified strand. Duocarmycin adopts an extended conformation and is aligned at approximately 45 degrees to the helix axis with its non-polar concave edges interacting with the floor of the minor groove while its polar edges are sandwiched within the walls of the minor groove. The T3.*A12+ modification site pair forms a weak central Watson-Crick hydrogen bond in contrast to all A.T and G.C pairs, which align through standard Watson-Crick pairing in the complex. The helical parameters are consistent with a minimally perturbed right-handed duplex in the complex with minor groove width and x-displacement parameters indicative of a B-form helix. A striking feature of the complex is the positioning of duocarmycin A within the walls of the minor groove resulting in upfield shifts of the minor groove sugar protons, as well as backbone proton and phosphorus resonances in the DNA segment spanning the binding site.
Organizational Affiliation:
Cellular Biochemistry and Biophysics Program, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY 10021, USA.