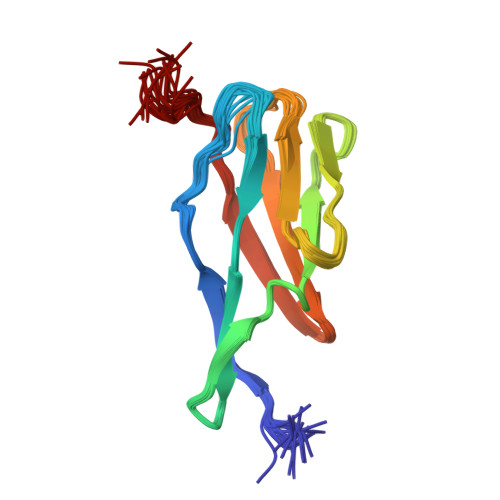
NMR Solution Structure of the Terminal Immunoglobulin-like Domain from the Leptospira Host-Interacting Outer Membrane Protein, LigB.
Ptak, C.P., Hsieh, C.L., Lin, Y.P., Maltsev, A.S., Raman, R., Sharma, Y., Oswald, R.E., Chang, Y.F.(2014) Biochemistry 53: 5249-5260
- PubMed: 25068811
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi500669u
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2MOG - PubMed Abstract:
A number of surface proteins specific to pathogenic strains of Leptospira have been identified. The Lig protein family has shown promise as a marker in typing leptospiral isolates for pathogenesis and as an antigen in vaccines. We used NMR spectroscopy to solve the solution structure of the twelfth immunoglobulin-like (Ig-like) repeat domain from LigB (LigB-12). The fold is similar to that of other bacterial Ig-like domains and comprised mainly of β-strands that form a β-sandwich based on a Greek-key folding arrangement. Based on sequence analysis and conservation of structurally important residues, homology models for the other LigB Ig-like domains were generated. The set of LigB models illustrates the electrostatic differences between the domains as well as the possible interactions between neighboring domains. Understanding the structure of the extracellular portion of LigB and related proteins is important for developing diagnostic methods and new therapeutics directed toward leptospirosis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Population Medicine and Diagnostic Sciences and ‡Department of Molecular Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell University , Ithaca, New York 14853, United States.