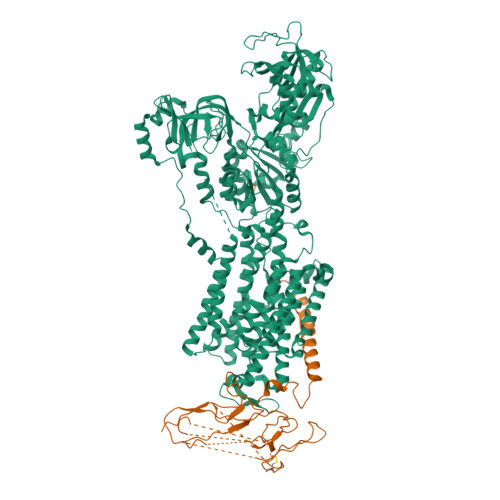
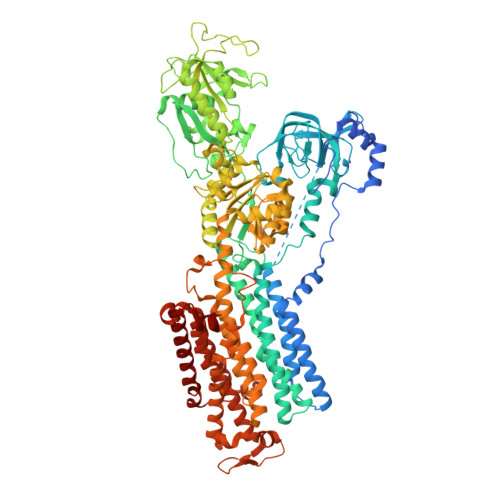
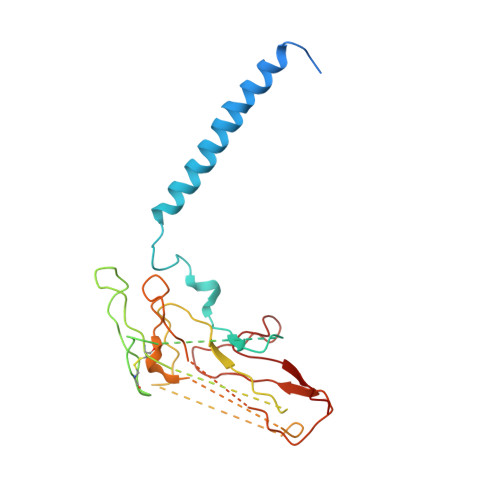
Conformational Rearrangement of Gastric H(+),K(+)- ATPase Induced by an Acid Suppressant.
Abe, K., Tani, K., Fujiyoshi, Y.(2011) Nat Commun 2: 155
- PubMed: 21224846
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1154
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2XZB - PubMed Abstract:
Acid-related gastric diseases are associated with disorder of digestive tract acidification. The gastric proton pump, H(+),K(+)-ATPase, exports H(+) in exchange for luminal K(+) to generate a highly acidic environment in the stomach, and is a main target for acid suppressants. Here, we report the three-dimensional structure of gastric H(+),K(+)-ATPase with bound SCH28080, a representative K(+)-competitive acid blocker, at 7 Å resolution based on electron crystallography of two-dimensional crystals. The density of the bound SCH28080 is found near transmembrane (TM) helices 4, 5 and 6, in the luminal cavity. The SCH28080-binding site is formed by the rearrangement of TM helices, which is in turn transmitted to the cytoplasmic domains, resulting in a luminal-open conformation. These results represent the first structural evidence for a binding site of an acid suppressant on H(+),K(+)-ATPase, and the conformational change induced by this class of drugs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biophysics, Faculty of Science, Kyoto University, Oiwake, Kitashirakawa, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606-0852, Japan.