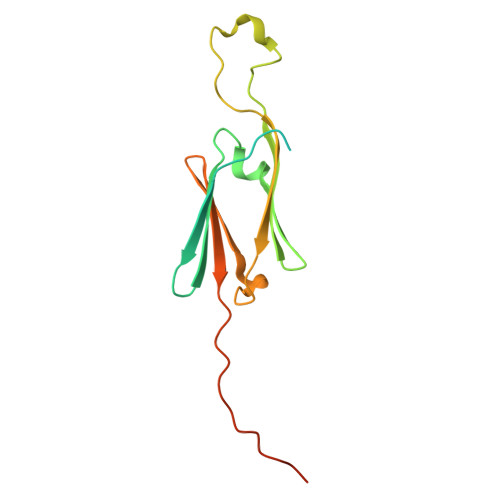
Crystal structure of a small heat-shock protein from Xylella fastidiosa reveals a distinct high-order structure.
Fonseca, E.M., Scorsato, V., Dos Santos, M.L., Junior, A.T., Tada, S.F., Dos Santos, C.A., de Toledo, M.A., de Souza, A.P., Polikarpov, I., Aparicio, R.(2017) Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun 73: 222-227
- PubMed: 28368281
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X17004101
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
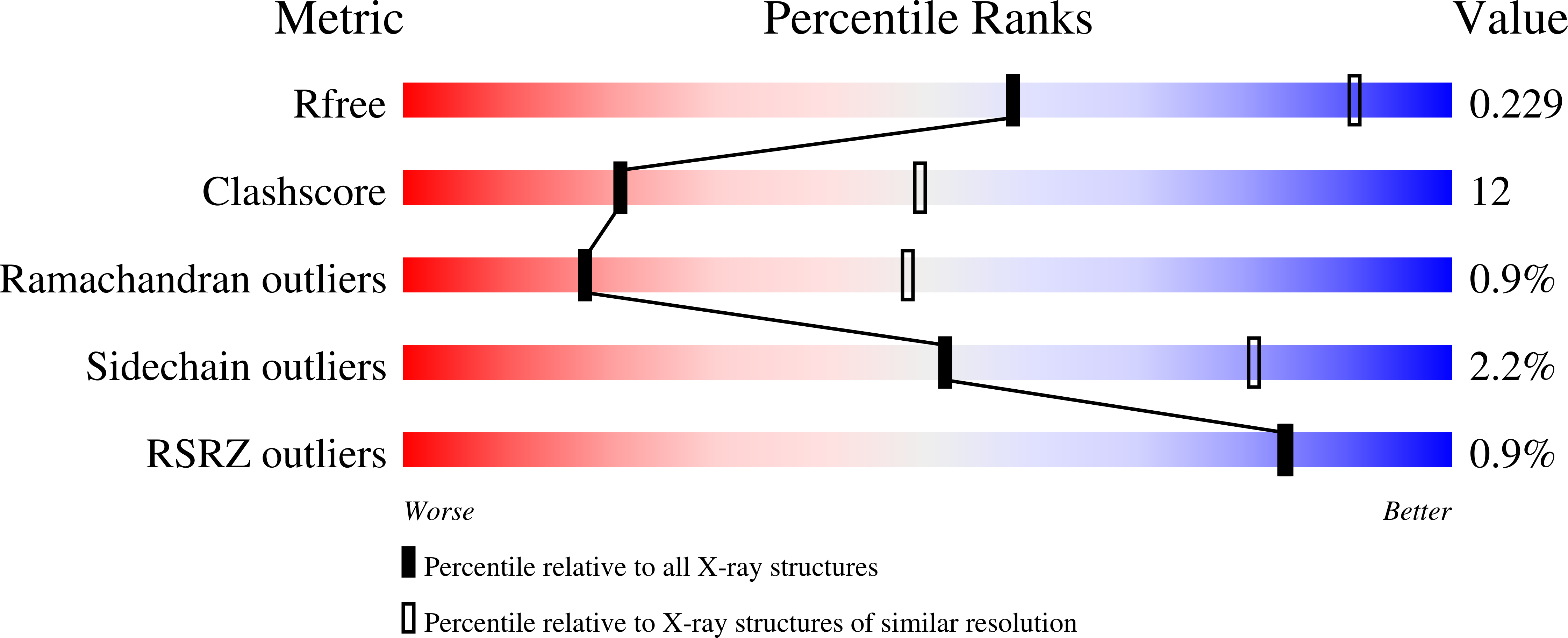
5J7N - PubMed Abstract:
Citrus variegated chlorosis is a disease that attacks economically important citrus plantations and is caused by the plant-pathogenic bacterium Xylella fastidiosa. In this work, the structure of a small heat-shock protein from X. fastidiosa (XfsHSP17.9) is reported. The high-order structures of small heat-shock proteins from other organisms are arranged in the forms of double-disc, hollow-sphere or spherical assemblies. Unexpectedly, the structure reported here reveals a high-order architecture forming a nearly square cavity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Structural Biology and Crystallography, Institute of Chemistry, University of Campinas, CP6154, 13083-970 Campinas-SP, Brazil.