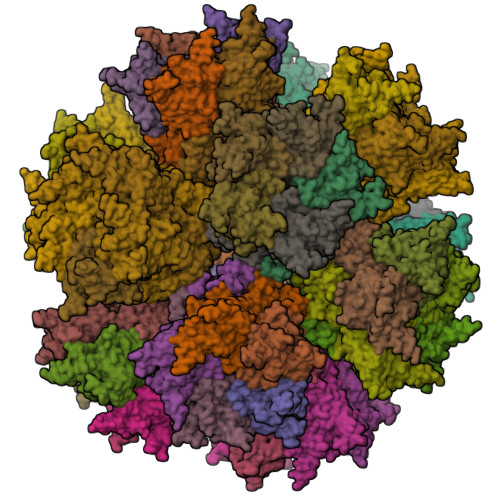
Synthetic self-assembling ADDomer platform for highly efficient vaccination by genetically encoded multiepitope display.
Vragniau, C., Bufton, J.C., Garzoni, F., Stermann, E., Rabi, F., Terrat, C., Guidetti, M., Josserand, V., Williams, M., Woods, C.J., Viedma, G., Bates, P., Verrier, B., Chaperot, L., Schaffitzel, C., Berger, I., Fender, P.(2019) Sci Adv 5: eaaw2853-eaaw2853
- PubMed: 31620562
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaw2853
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6HCR - PubMed Abstract:
Self-assembling virus-like particles represent highly attractive tools for developing next-generation vaccines and protein therapeutics. We created ADDomer, an adenovirus-derived multimeric protein-based self-assembling nanoparticle scaffold engineered to facilitate plug-and-play display of multiple immunogenic epitopes from pathogens. We used cryo-electron microscopy at near-atomic resolution and implemented novel, cost-effective, high-performance cloud computing to reveal architectural features in unprecedented detail. We analyzed ADDomer interaction with components of the immune system and developed a promising first-in-kind ADDomer-based vaccine candidate to combat emerging Chikungunya infectious disease, exemplifying the potential of our approach.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institut de Biologie Structurale (IBS), Université Grenoble Alpes, CNRS, CEA, 71 Avenue des Martyrs, 38042 Grenoble, France.