Phosphorylation of the alpha-I motif in SYMRK drives root nodule organogenesis.
Abel, N.B., Norgaard, M.M.M., Hansen, S.B., Gysel, K., Diez, I.A., Jensen, O.N., Stougaard, J., Andersen, K.R.(2024) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 121: e2311522121-e2311522121
- PubMed: 38363863
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2311522121
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
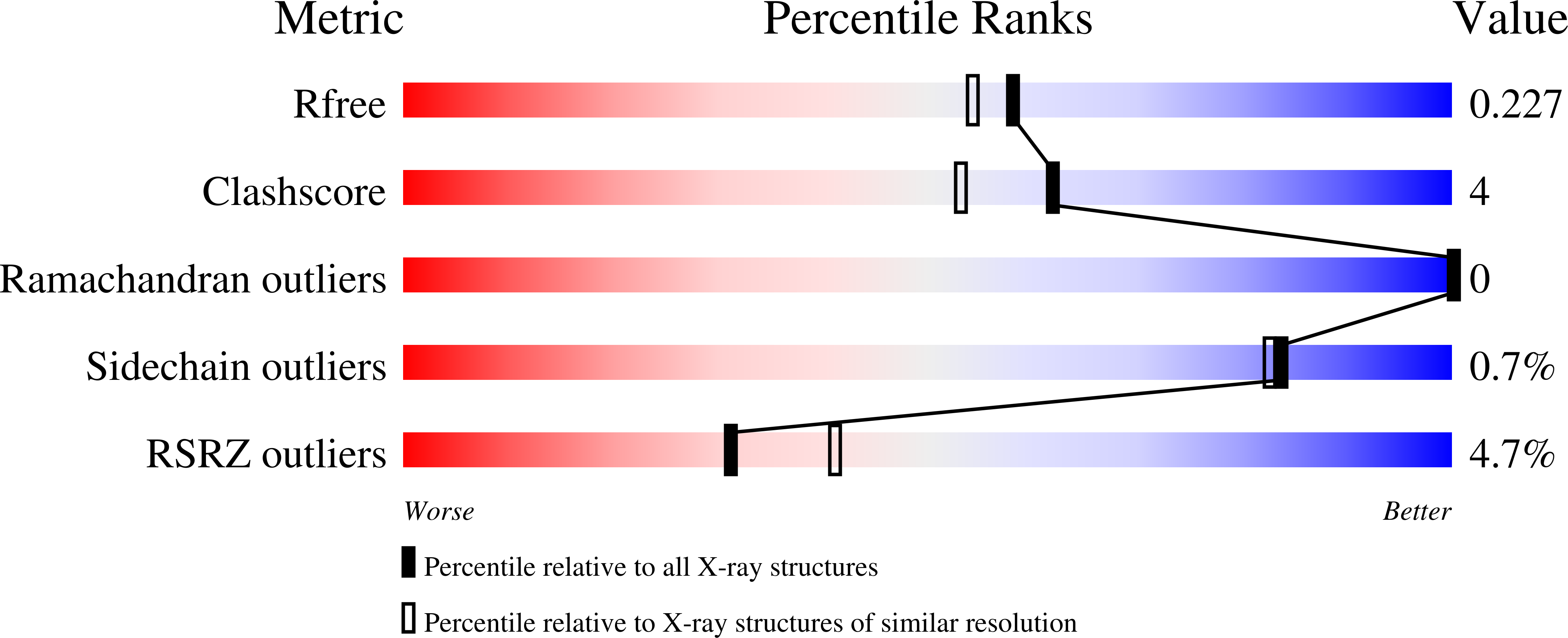
8PEH - PubMed Abstract:
Symbiosis receptor-like kinase SYMRK is required for root nodule symbiosis between legume plants and nitrogen-fixing bacteria. To understand symbiotic signaling from SYMRK, we determined the crystal structure to 1.95 Å and mapped the phosphorylation sites onto the intracellular domain. We identified four serine residues in a conserved "alpha-I" motif, located on the border between the kinase core domain and the flexible C-terminal tail, that, when phosphorylated, drives organogenesis. Substituting the four serines with alanines abolished symbiotic signaling, while substituting them with phosphorylation-mimicking aspartates induced the formation of spontaneous nodules in the absence of bacteria. These findings show that the signaling pathway controlling root nodule organogenesis is mediated by SYMRK phosphorylation, which may help when engineering this trait into non-legume plants.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics, Aarhus University, Aarhus C 8000, Denmark.