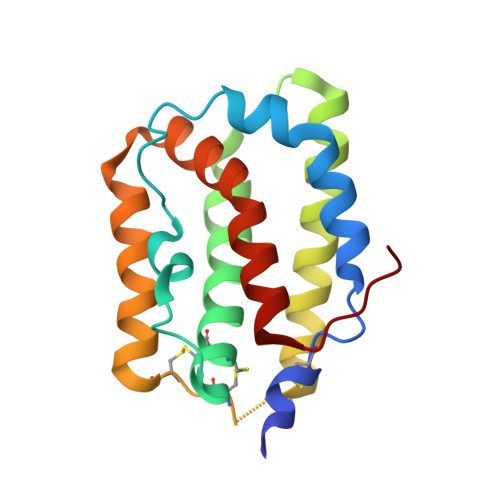
Crystal structure of interleukin-19 defines a new subfamily of helical cytokines
Chang, C., Magracheva, E., Kozlov, S., Fong, S., Tobin, G., Kotenko, S., Wlodawer, A., Zdanov, A.(2003) J Biol Chem 278: 3308-3313
- PubMed: 12403790
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M208602200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1N1F - PubMed Abstract:
Interleukin-19 (IL-19) is a novel cytokine that was initially identified during a sequence data base search aimed at finding potential IL-10 homologs. IL-19 shares a receptor complex with IL-20, indicating that the biological activities of these two cytokines overlap and that both may play an important role in regulating development and proper functioning of the skin. We determined the crystal structure of human recombinant IL-19 and refined it at 1.95-A resolution to an R-factor of 0.157. Unlike IL-10, which forms an intercalated dimer, the molecule of IL-19 is a monomer made of seven amphipathic helices, A-G, creating a unique helical bundle. On the basis of the observed structure, we propose that IL-19, IL-20, and other putative members of the proposed IL-10 family together form a distinct subfamily of helical cytokines.
Organizational Affiliation:
Protein Structure Section, Macromolecular Crystallography Laboratory, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute-Frederick, National Institutes of Health, Maryland 21702-1201, USA.