Proteomics-based target identification: bengamides as a new class of methionine aminopeptidase inhibitors.
Towbin, H., Bair, K.W., DeCaprio, J.A., Eck, M.J., Kim, S., Kinder, F.R., Morollo, A., Mueller, D.R., Schindler, P., Song, H.K., van Oostrum, J., Versace, R.W., Voshol, H., Wood, J., Zabludoff, S., Phillips, P.E.(2003) J Biol Chem 278: 52964-52971
- PubMed: 14534293
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M309039200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1QZY - PubMed Abstract:
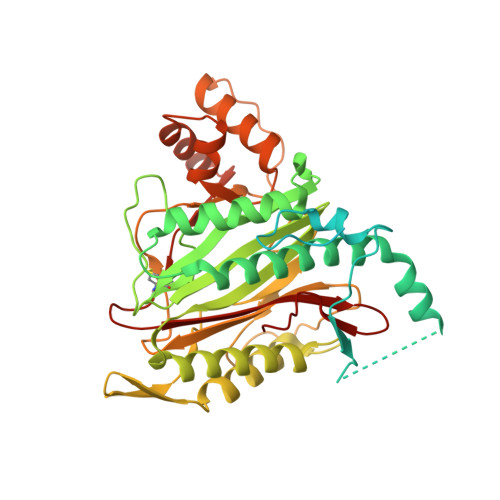
LAF389 is a synthetic analogue of bengamides, a class of marine natural products that produce inhibitory effects on tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. A proteomics-based approach has been used to identify signaling pathways affected by bengamides. LAF389 treatment of cells resulted in altered mobility of a subset of proteins on two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Detailed analysis of one of the proteins, 14-3-3gamma, showed that bengamide treatment resulted in retention of the amino-terminal methionine, suggesting that bengamides directly or indirectly inhibited methionine aminopeptidases (MetAps). Both known MetAps are inhibited by LAF389. Short interfering RNA suppression of MetAp2 also altered amino-terminal processing of 14-3-3gamma. A high resolution structure of human MetAp2 co-crystallized with a bengamide shows that the compound binds in a manner that mimics peptide substrates. Additionally, the structure reveals that three key hydroxyl groups on the inhibitor coordinate the di-cobalt center in the enzyme active site.
Organizational Affiliation:
Novartis Pharma AG, CH-4036 Basle, Switzerland.