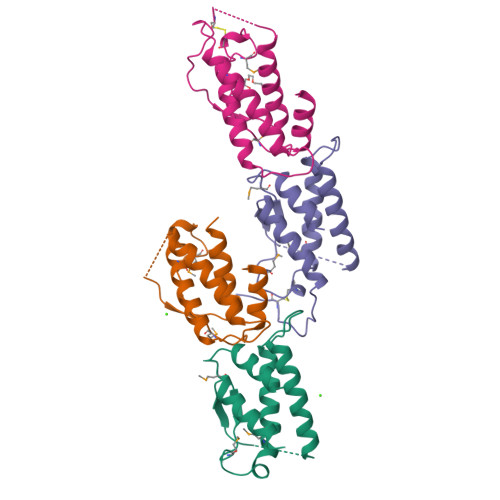
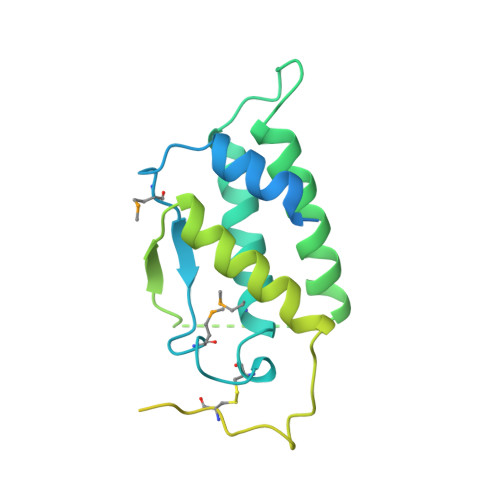
Structure of the active core of human stem cell factor and analysis of binding to its receptor kit.
Jiang, X., Gurel, O., Mendiaz, E.A., Stearns, G.W., Clogston, C.L., Lu, H.S., Osslund, T.D., Syed, R.S., Langley, K.E., Hendrickson, W.A.(2000) EMBO J 19: 3192-3203
- PubMed: 10880433
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/19.13.3192
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1SCF - PubMed Abstract:
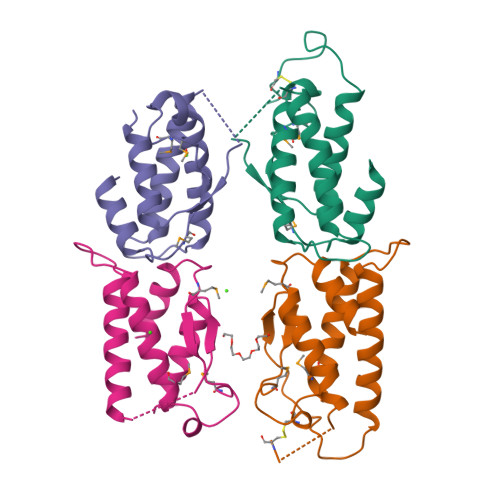
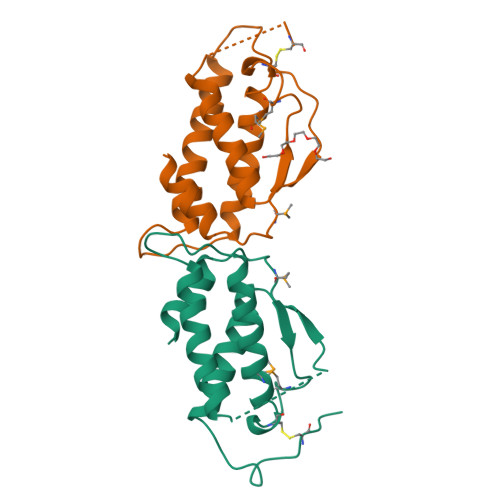
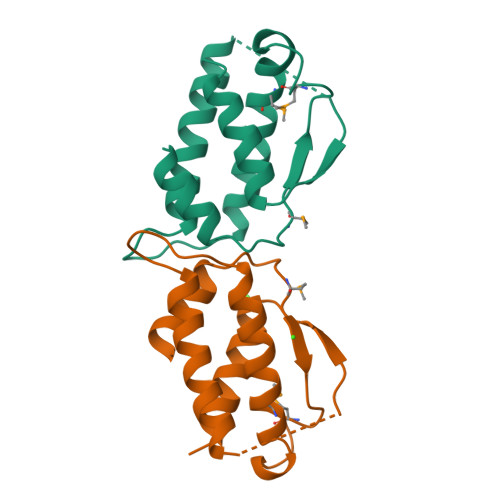
Stem cell factor (SCF) is an early-acting hematopoietic cytokine that elicits multiple biological effects. SCF is dimeric and occurs in soluble and membrane-bound forms. It transduces signals by ligand- mediated dimerization of its receptor, Kit, which is a receptor tyrosine kinase related to the receptors for platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), macrophage colony-stimulating factor, Flt-3 ligand and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). All of these have extracellular ligand-binding portions composed of immunoglobulin-like repeats. We have determined the crystal structure of selenomethionyl soluble human SCF at 2.2 A resolution by multiwavelength anomalous diffraction phasing. SCF has the characteristic helical cytokine topology, but the structure is unique apart from core portions. The SCF dimer has a symmetric 'head-to-head' association. Using various prior observations, we have located potential Kit-binding sites on the SCF dimer. A superimposition of this dimer onto VEGF in its complex with the receptor Flt-1 places the binding sites on SCF in positions of topographical and electrostatic complementarity with the Kit counterparts of Flt-1, and a similar model can be made for the complex of PDGF with its receptor.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics and Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Columbia University, New York, NY 10032, USA.