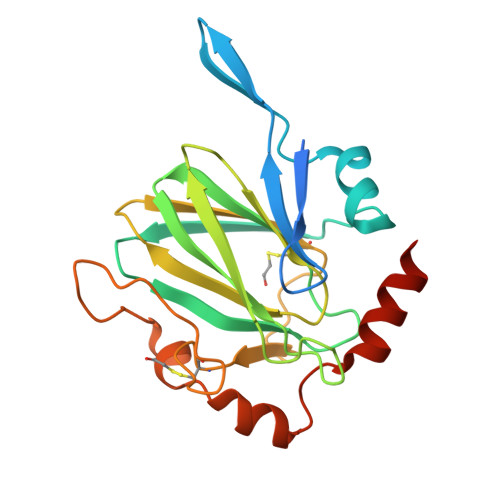
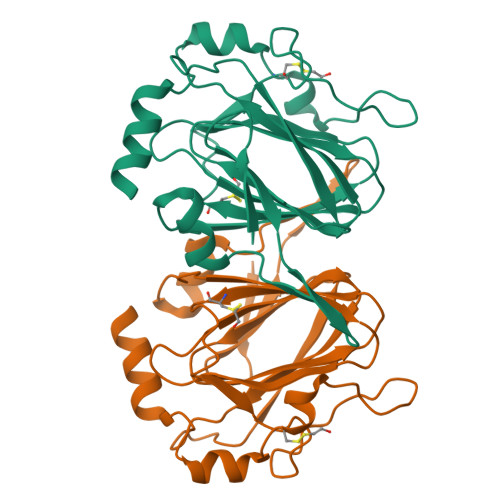
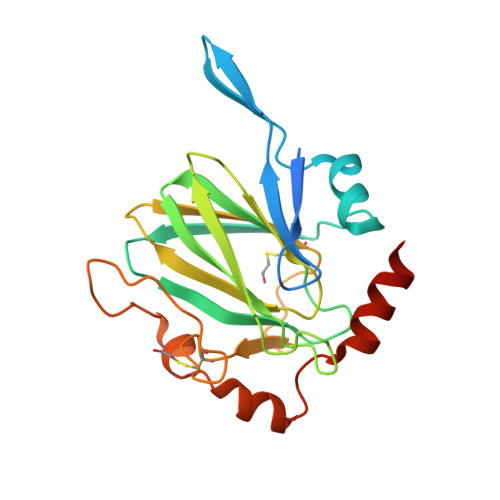
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Rmlc Epimerase (Rv3465): A Promising Drug-Target Structure in the Rhamnose Pathway
Kantardjieff, K.A., Kim, C.-Y., Naranjo, C., Waldo, G.S., Lekin, T., Segelke, B.W., Zemla, A., Park, M.S., Terwilliger, T., Rupp, B.(2004) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 60: 895
- PubMed: 15103135
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444904005323
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1UPI - PubMed Abstract:
The Mycobacterium tuberculosis rmlC gene encodes dTDP-4-keto-6-deoxyglucose epimerase, the third enzyme in the M. tuberculosis dTDP-L-rhamnose pathway which is essential for mycobacterial cell-wall synthesis. Because it is structurally unique, highly substrate-specific and does not require a cofactor, RmlC is considered to be the most promising drug target in the pathway, and the M. tuberculosis rmlC gene was selected in the initial round of TB Structural Genomics Consortium targets for structure determination. The 1.7 A native structure determined by the consortium facilities is reported and implications for in silico screening of ligands for structure-guided drug design are discussed.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry and W M Keck Foundation Center for Molecular Structure, California State University Fullerton, Fullerton, CA 92834, USA.