High resolution crystal structure of human Rab9 GTPase: A novel antiviral drug target
Chen, L., DiGiammarino, E., Zhou, X.E., Wang, Y., Toh, D., Hodge, T.W., Meehan, E.J.(2004) J Biological Chem 279: 40204-40208
- PubMed: 15263003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M407114200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1WMS - PubMed Abstract:
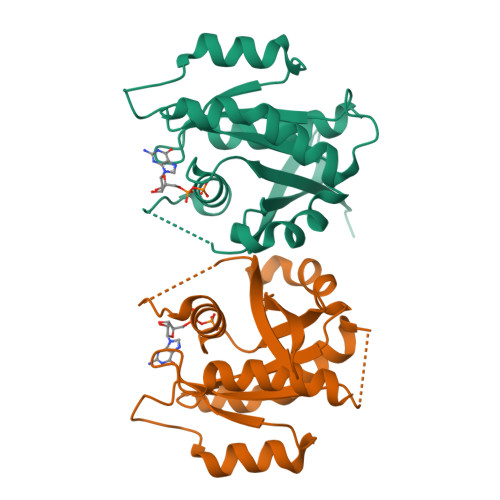
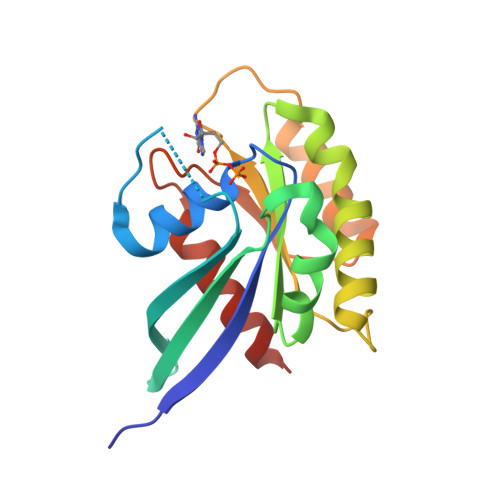
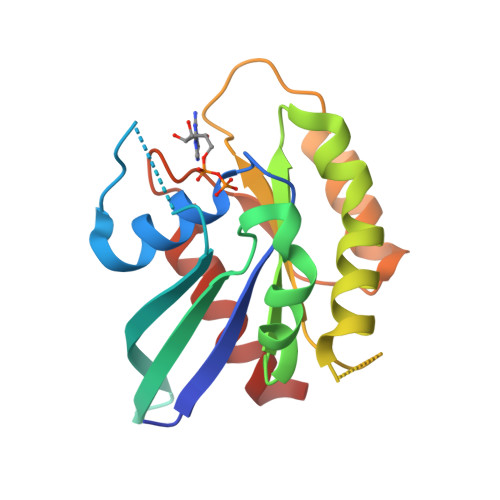
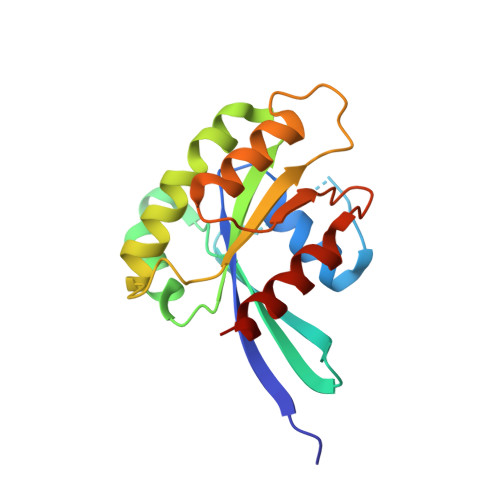
Rab GTPases and their effectors facilitate vesicular transport by tethering donor vesicles to their respective target membranes. Rab9 mediates late endosome to trans-Golgi transport and has recently been found to be a key cellular component for human immunodeficiency virus-1, Ebola, Marburg, and measles virus replication, suggesting that it may be a novel target in the development of broad spectrum antiviral drugs. As part of our structure-based drug design program, we have determined the crystal structure of a C-terminally truncated human Rab9 (residues 1-177) to 1.25-A resolution. The overall structure shows a characteristic nucleotide binding fold consisting of a six-stranded beta-sheet surrounded by five alpha-helices with a tightly bound GDP molecule in the active site. Structure-based sequence alignment of Rab9 with other Rab proteins reveals that its active site consists of residues highly conserved in the Rab GTPase family, implying a common catalytic mechanism. However, Rab9 contains seven regions that are significantly different in conformation from other Rab proteins. Some of those regions coincide with putative effector-binding sites and switch I and switch II regions identified by structure/sequence alignments. The Rab9 structure at near atomic resolution provides an excellent model for structure-based antiviral drug design.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory for Structural Biology, Department of Chemistry, Graduate Programs of Biotechnology, Chemistry and Materials Science, University of Alabama in Huntsville, Huntsville, Alabama 35899, USA.