The Rac1 Polybasic Region Is Required for Interaction with Its Effector PRK1
Modha, R., Campbell, L.J., Nietlispach, D., Buhecha, H.R., Owen, D., Mott, H.R.(2008) J Biological Chem 283: 1492-1500
- PubMed: 18006505
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M706760200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2RMK - PubMed Abstract:
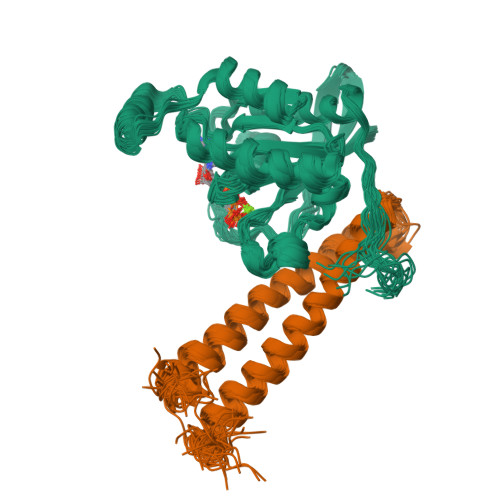
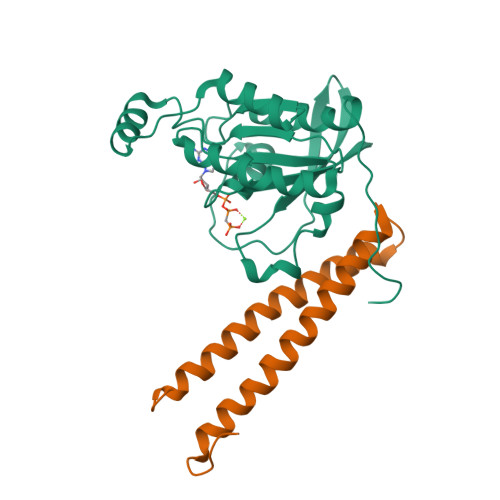
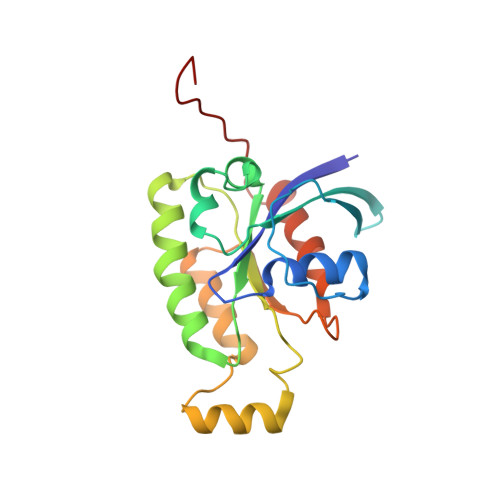
Protein kinase C-related kinase 1 (PRK1 or PKN) is involved in regulation of the intermediate filaments of the actin cytoskeleton, as well as having effects on processes as diverse as mitotic timing and apoptosis. It is activated by interacting with the Rho family small G proteins and arachidonic acid or by caspase cleavage. We have previously shown that the HR1b of PRK1 binds exclusively to Rac1, whereas the HR1a domain binds to both Rac1 and RhoA. Here, we have determined the solution structure of the HR1b-Rac complex. We show that HR1b binds to the C-terminal end of the effector loop and switch 2 of Rac1. Comparison with the HR1a-RhoA structure shows that this part of the Rac1-HR1b interaction is homologous to one of the contact sites that HR1a makes with RhoA. The Rac1 used in this study included the C-terminal polybasic region, which is frequently omitted from structural studies, as well as the core G domain. The Rac1 C-terminal region reverses in direction to interact with residues in switch 2, and the polybasic region itself interacts with residues in HR1b. The interactions with HR1b do not prevent the polybasic region being available to contact the negatively charged membrane phospholipids, which is considered to be its primary role. This is the first structural demonstration that the C terminus of a G protein forms a novel recognition element for effector binding.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Cambridge, 80, Tennis Court Road, Cambridge CB2 1GA, United Kingdom.