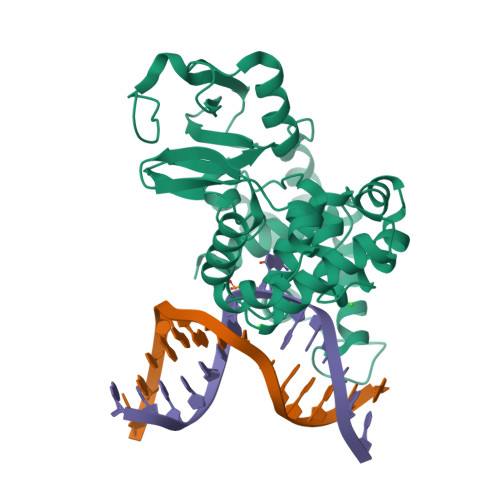
Separation-of-Function Mutants Unravel the Dual- Reaction Mode of Human 8-Oxoguanine DNA Glycosylase.
Dalhus, B., Forsbring, M., Helle, I.H., Vik, E.S., Forstrom, R.J., Backe, P.H., Alseth, I., Bjoras, M.(2011) Structure 19: 117
- PubMed: 21220122
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2010.09.023
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2XHI - PubMed Abstract:
7,8-Dihydro-8-oxoguanine (8oxoG) is a major mutagenic base lesion formed when reactive oxygen species react with guanine in DNA. The human 8oxoG DNA glycosylase (hOgg1) recognizes and initiates repair of 8oxoG. hOgg1 is acknowledged as a bifunctional DNA glycosylase catalyzing removal of the damaged base followed by cleavage of the backbone of the intermediate abasic DNA (AP lyase/β-elimination). When acting on 8oxoG-containing DNA, these two steps in the hOgg1 catalysis are considered coupled, with Lys249 implicated as a key residue. However, several lines of evidence point to a concurrent and independent monofunctional hydrolysis of the N-glycosylic bond being the in vivo relevant reaction mode of hOgg1. Here, we present biochemical and structural evidence for the monofunctional mode of hOgg1 by design of separation-of-function mutants. Asp268 is identified as the catalytic residue, while Lys249 appears critical for the specific recognition and final alignment of 8oxoG during the hydrolysis reaction.
Organizational Affiliation:
Centre for Molecular Biology and Neuroscience and Institute of Medical Microbiology, Rikshospitalet, Oslo University Hospital, N-0027 Oslo, Norway. bjorn.dalhus@rr-research.no