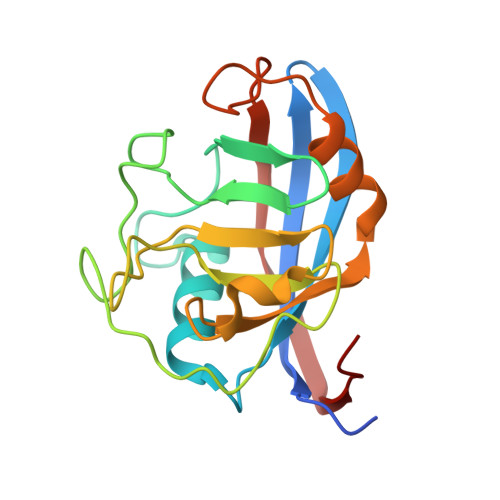
Structural Basis of Cyclophilin B Binding by the Calnexin/Calreticulin P-domain.
Kozlov, G., Bastos-Aristizabal, S., Maattanen, P., Rosenauer, A., Zheng, F., Killikelly, A., Trempe, J.F., Thomas, D.Y., Gehring, K.(2010) J Biological Chem 285: 35551-35557
- PubMed: 20801878
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.160101
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3ICH, 3ICI - PubMed Abstract:
Little is known about how chaperones in the endoplasmic reticulum are organized into complexes to assist in the proper folding of secreted proteins. One notable exception is the complex of ERp57 and calnexin that functions as part the calnexin cycle to direct disulfide bond formation in N-glycoproteins. Here, we report three new complexes composed of the peptidyl prolyl cis-trans-isomerase cyclophilin B and any of the lectin chaperones: calnexin, calreticulin, or calmegin. The 1.7 Å crystal structure of cyclophilin with the proline-rich P-domain of calmegin reveals that binding is mediated by the same surface that binds ERp57. We used NMR titrations and mutagenesis to measure low micromolar binding of cyclophilin to all three lectin chaperones and identify essential interfacial residues. The immunosuppressant cyclosporin A did not affect complex formation, confirming the functional independence of the P-domain binding and proline isomerization sites of cyclophilin. Our results reveal the P-domain functions as a unique protein-protein interaction domain and implicate a peptidyl prolyl isomerase as a new element in the calnexin cycle.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Groupe de Recherche Axé sur la Structure des Protéines, McGill University, Montréal, Québec H3G 0B1, Canada.