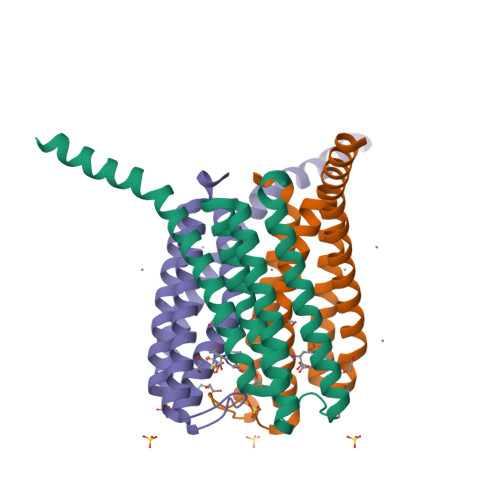
The catalytic architecture of leukotriene C4 synthase with two arginine residues
Saino, H., Ukita, Y., Ago, H., Irikura, D., Nisawa, A., Ueno, G., Yamamoto, M., Kanaoka, Y., Lam, B.K., Austen, K.F., Miyano, M.(2011) J Biological Chem 286: 16392-16401
- PubMed: 21454538
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.150177
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3PCV - PubMed Abstract:
Leukotriene (LT) C(4) and its metabolites, LTD(4) and LTE(4), are involved in the pathobiology of bronchial asthma. LTC(4) synthase is the nuclear membrane-embedded enzyme responsible for LTC(4) biosynthesis, catalyzing the conjugation of two substrates that have considerably different water solubility; that amphipathic LTA(4) as a derivative of arachidonic acid and a water-soluble glutathione (GSH). A previous crystal structure revealed important details of GSH binding and implied a GSH activating function for Arg-104. In addition, Arg-31 was also proposed to participate in the catalysis based on the putative LTA(4) binding model. In this study enzymatic assay with mutant enzymes demonstrates that Arg-104 is required for the binding and activation of GSH and that Arg-31 is needed for catalysis probably by activating the epoxide group of LTA(4).
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biophysics Laboratory, RIKEN SPring-8 Center, Harima Institute, Sayo, Hyogo, Japan.