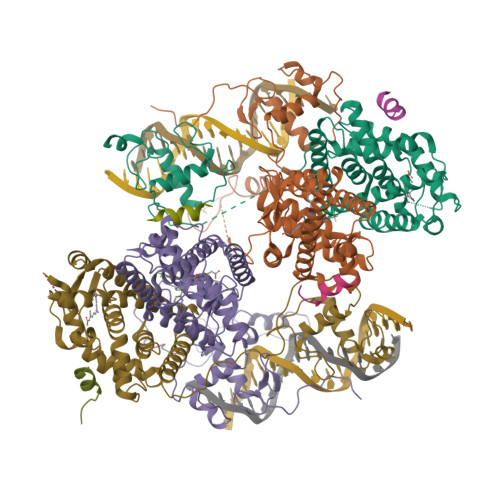
Structure of the retinoid X receptor alpha-liver X receptor beta (RXR alpha-LXR beta ) heterodimer on DNA.
Lou, X., Toresson, G., Benod, C., Suh, J.H., Philips, K.J., Webb, P., Gustafsson, J.A.(2014) Nat Struct Mol Biol 21: 277-281
- PubMed: 24561505
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2778
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4NQA - PubMed Abstract:
Nuclear receptors (NRs) are conditional transcription factors with common multidomain organization that bind diverse DNA elements. How DNA sequences influence NR conformation is poorly understood. Here we report the crystal structure of the human retinoid X receptor α-liver X receptor β (RXRα-LXRβ) heterodimer on its cognate element, an AGGTCA direct repeat spaced by 4 nt. The complex has an extended X-shaped arrangement, with DNA- and ligand-binding domains crossed, in contrast to the parallel domain arrangement of other NRs that bind an AGGTCA direct repeat spaced by 1 nt. The LXRβ core binds DNA via canonical contacts and auxiliary DNA contacts that enhance affinity for the response element. Comparisons of RXRα-LXRβs in the crystal asymmetric unit and with previous NR structures reveal flexibility in NR organization and suggest a role for RXRα in adaptation of heterodimeric complexes to DNA.
Organizational Affiliation:
1] Center for Nuclear Receptors and Cell Signaling, University of Houston, Houston, Texas, USA. [2] Genomic Medicine Program, Houston Methodist Research Institute, Houston, Texas, USA.