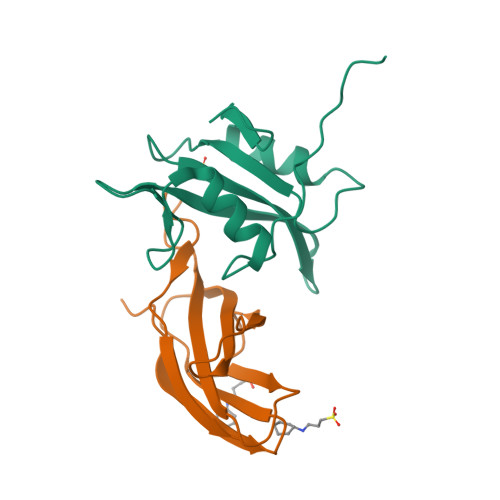
Selective Targeting of SH2 Domain-Phosphotyrosine Interactions of Src Family Tyrosine Kinases with Monobodies.
Kukenshoner, T., Schmit, N.E., Bouda, E., Sha, F., Pojer, F., Koide, A., Seeliger, M., Koide, S., Hantschel, O.(2017) J Mol Biology 429: 1364-1380
- PubMed: 28347651
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2017.03.023
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5MTJ, 5MTM, 5MTN - PubMed Abstract:
The binding of Src-homology 2 (SH2) domains to phosphotyrosine (pY) sites is critical for the autoinhibition and substrate recognition of the eight Src family kinases (SFKs). The high sequence conservation of the 120 human SH2 domains poses a significant challenge to selectively perturb the interactions of even the SFK SH2 family against the rest of the SH2 domains. We have developed synthetic binding proteins, termed monobodies, for six of the SFK SH2 domains with nanomolar affinity. Most of these monobodies competed with pY ligand binding and showed strong selectivity for either the SrcA (Yes, Src, Fyn, Fgr) or SrcB subgroup (Lck, Lyn, Blk, Hck). Interactome analysis of intracellularly expressed monobodies revealed that they bind SFKs but no other SH2-containing proteins. Three crystal structures of monobody-SH2 complexes unveiled different and only partly overlapping binding modes, which rationalized the observed selectivity and enabled structure-based mutagenesis to modulate inhibition mode and selectivity. In line with the critical roles of SFK SH2 domains in kinase autoinhibition and T-cell receptor signaling, monobodies binding the Src and Hck SH2 domains selectively activated respective recombinant kinases, whereas an Lck SH2-binding monobody inhibited proximal signaling events downstream of the T-cell receptor complex. Our results show that SFK SH2 domains can be targeted with unprecedented potency and selectivity using monobodies. They are excellent tools for dissecting SFK functions in normal development and signaling and to interfere with aberrant SFK signaling networks in cancer cells.
Organizational Affiliation:
Swiss Institute for Experimental Cancer Research (ISREC), School of Life Sciences, École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Station 19, 1015 Lausanne, Switzerland.