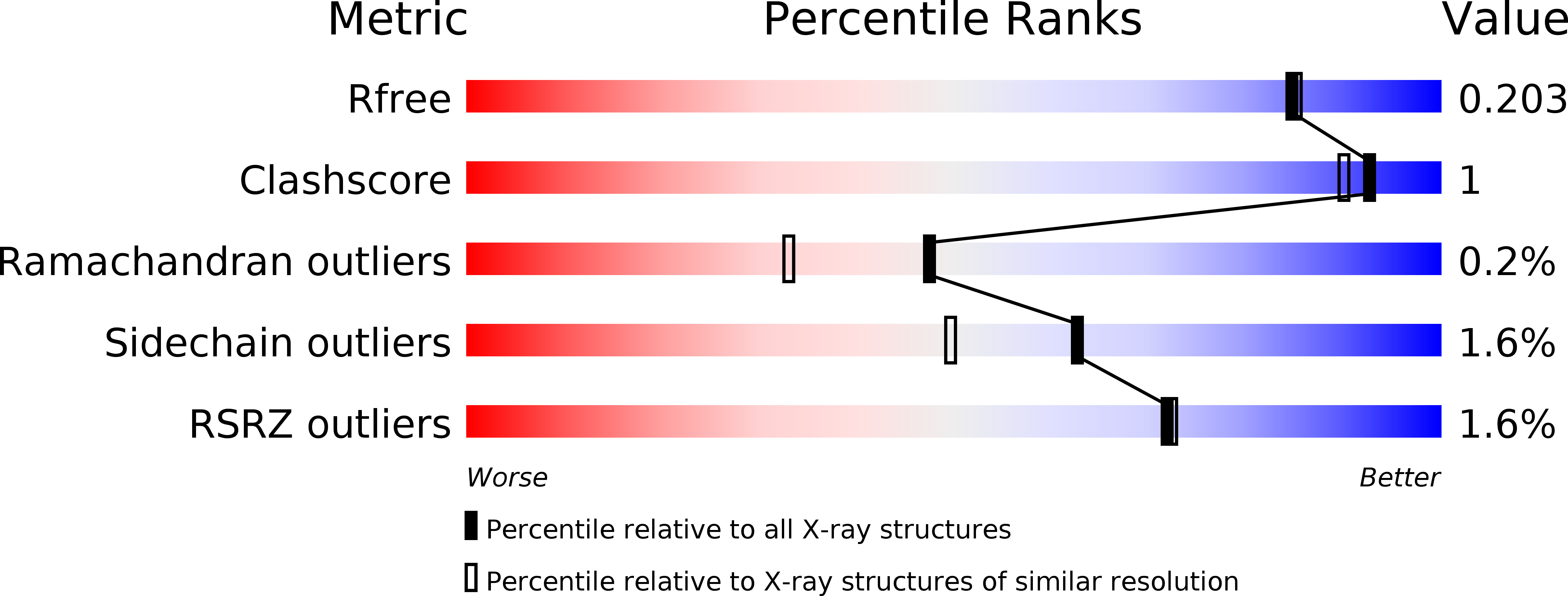
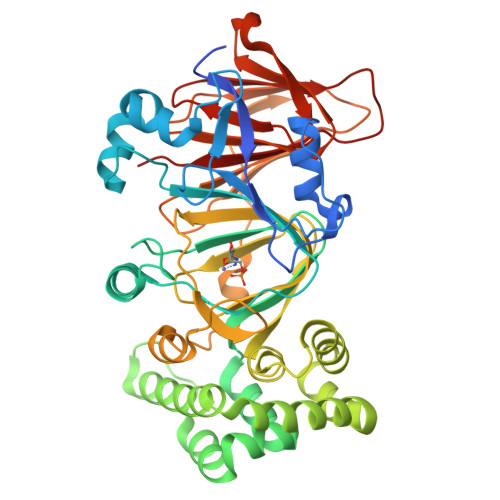
Crystal structure of phosphomannose isomerase from Candida albicans complexed with 5-phospho-d-arabinonhydrazide.
Ahmad, L., Plancqueel, S., Dubosclard, V., Lazar, N., Ghattas, W., Li de la Sierra-Gallay, I., van Tilbeurgh, H., Salmon, L.(2018) FEBS Lett 592: 1667-1680
- PubMed: 29687459
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13059
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5NW7 - PubMed Abstract:
Type I phosphomannose isomerases (PMIs) are zinc-dependent monofunctional metalloenzymes catalysing the reversible isomerization of d-mannose 6-phosphate to d-fructose 6-phosphate. 5-Phospho-d-arabinonhydrazide (5PAHz), designed as an analogue of the enediolate high-energy intermediate, strongly inhibits PMI from Candida albicans (CaPMI). In this study, we report the 3D crystal structure of CaPMI complexed with 5PAHz at 1.85 Å resolution. The high-resolution structure suggests that Glu294 is the catalytic base that transfers a proton between the C1 and C2 carbon atoms of the substrate. Bidentate coordination of the inhibitor explains the stereochemistry of the isomerase activity, as well as the absence of both anomerase and C2-epimerase activities for Type I PMIs. A detailed mechanism of the reversible isomerization is proposed.
Organizational Affiliation:
Equipe de Chimie Bioorganique et Bioinorganique, Institut de Chimie Moléculaire et des Matériaux d'Orsay (ICMMO), CNRS UMR8182, LabEx LERMIT, Université Paris-Saclay, Université Paris-Sud, Orsay, France.