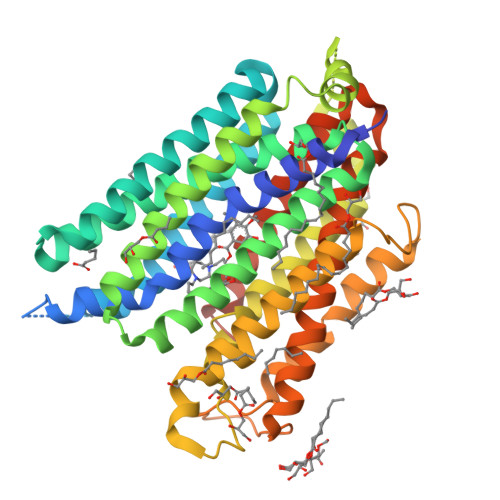
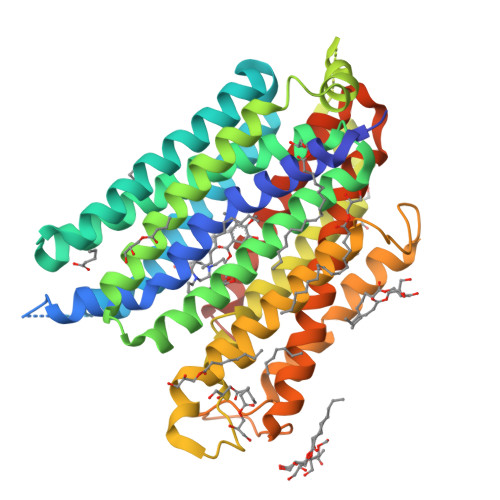
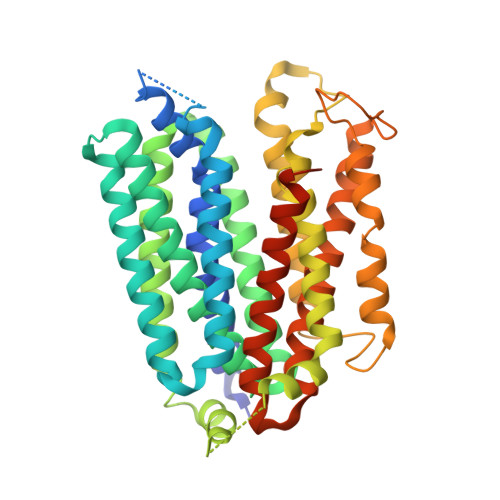
Structures of human ENT1 in complex with adenosine reuptake inhibitors.
Wright, N.J., Lee, S.Y.(2019) Nat Struct Mol Biol 26: 599-606
- PubMed: 31235912
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-019-0245-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6OB6, 6OB7 - PubMed Abstract:
The human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 (hENT1), a member of the SLC29 family, plays crucial roles in adenosine signaling, cellular uptake of nucleoside for DNA and RNA synthesis, and nucleoside-derived anticancer and antiviral drug transport in humans. Because of its central role in adenosine signaling, it is the target of adenosine reuptake inhibitors (AdoRI), several of which are used clinically. Despite its importance in human physiology and pharmacology, the molecular basis of hENT1-mediated adenosine transport and its inhibition by AdoRIs are limited, owing to the absence of structural information on hENT1. Here, we present crystal structures of hENT1 in complex with two chemically distinct AdoRIs: dilazep and S-(4-nitrobenzyl)-6-thioinosine (NBMPR). Combined with mutagenesis study, our structural analyses elucidate two distinct inhibitory mechanisms exhibited on hENT1 and provide insight into adenosine recognition and transport. Our studies provide a platform for improved pharmacological intervention of adenosine and nucleoside analog drug transport by hENT1.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC, USA.