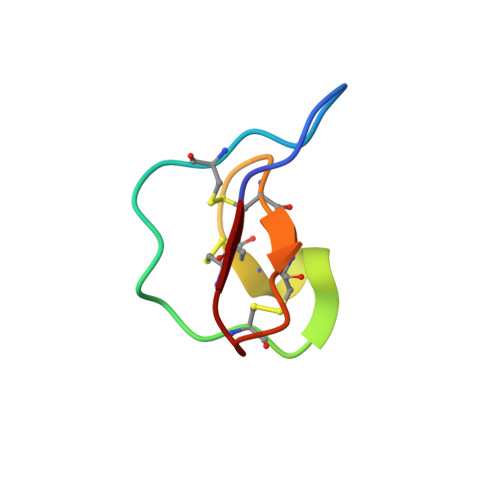
Circular proteins in plants: solution structure of a novel macrocyclic trypsin inhibitor from Momordica cochinchinensis.
Felizmenio-Quimio, M.E., Daly, N.L., Craik, D.J.(2001) J Biological Chem 276: 22875-22882
- PubMed: 11292835
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M101666200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1IB9 - PubMed Abstract:
Much interest has been generated by recent reports on the discovery of circular (i.e. head-to-tail cyclized) proteins in plants. Here we report the three-dimensional structure of one of the newest such circular proteins, MCoTI-II, a novel trypsin inhibitor from Momordica cochinchinensis, a member of the Cucurbitaceae plant family. The structure consists of a small beta-sheet, several turns, and a cystine knot arrangement of the three disulfide bonds. Interestingly, the molecular topology is similar to that of the plant cyclotides (Craik, D. J., Daly, N. L., Bond, T., and Waine, C. (1999) J. Mol. Biol. 294, 1327-1336), which derive from the Rubiaceae and Violaceae plant families, have antimicrobial activities, and exemplify the cyclic cystine knot structural motif as part of their circular backbone. The sequence, biological activity, and plant family of MCoTI-II are all different from known cyclotides. However, given the structural similarity, cyclic backbone, and plant origin of MCoTI-II, we propose that MCoTI-II can be classified as a new member of the cyclotide class of proteins. The expansion of the cyclotides to include trypsin inhibitory activity and a new plant family highlights the importance and functional variability of circular proteins and the fact that they are more common than has previously been believed. Insights into the possible roles of backbone cyclization have been gained by a comparison of the structure of MCoTI-II with the homologous acyclic trypsin inhibitors CMTI-I and EETI-II from the Cucurbitaceae plant family.
- Institute for Molecular Bioscience, University of Queensland, Brisbane, 4072 Queensland, Australia.
Organizational Affiliation: