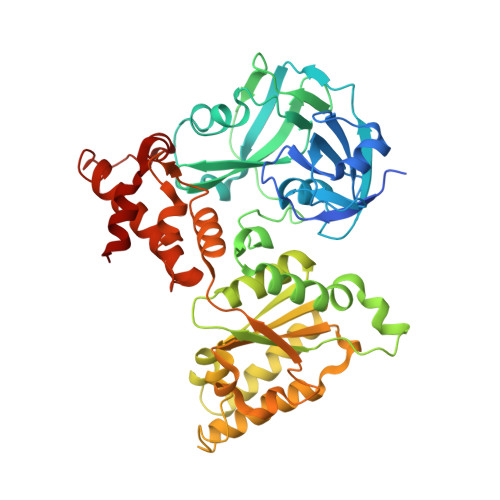
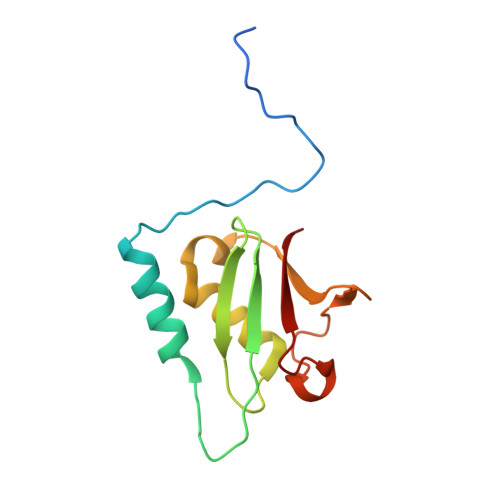
Structural basis of the interaction between the AAA ATPase p97/VCP and its adaptor protein p47.
Dreveny, I., Kondo, H., Uchiyama, K., Shaw, A., Zhang, X., Freemont, P.S.(2004) EMBO J 23: 1030-1039
- PubMed: 14988733
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600139
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1S3S - PubMed Abstract:
The AAA ATPase p97/VCP is involved in many cellular events including ubiquitin-dependent processes and membrane fusion. In the latter, the p97 adaptor protein p47 is of central importance. In order to provide insight into the molecular basis of p97 adaptor binding, we have determined the crystal structure of p97 ND1 domains complexed with p47 C-terminal domain at 2.9 A resolution. The structure reveals that the p47 ubiquitin regulatory X domain (UBX) domain interacts with the p97 N domain via a loop (S3/S4) that is highly conserved in UBX domains, but is absent in ubiquitin, which inserts into a hydrophobic pocket between the two p97 N subdomains. Deletion of this loop and point mutations in the loop significantly reduce p97 binding. This hydrophobic binding site is distinct from the predicted adaptor-binding site for the p97/VCP homologue N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor (NSF). Together, our data suggest that UBX domains may act as general p97/VCP/CDC48 binding modules and that adaptor binding for NSF and p97 might involve different binding sites. We also propose a classification for ubiquitin-like domains containing or lacking a longer S3/S4 loop.
- Centre for Structural Biology, Department of Biological Sciences, Imperial College London, South Kensington Campus, London, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: