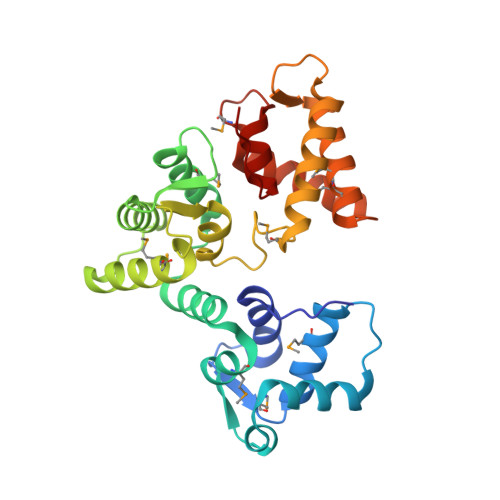
X-ray structure of Danio rerio secretagogin: A hexa-EF-hand calcium sensor.
Bitto, E., Bingman, C.A., Bittova, L., Frederick, R.O., Fox, B.G., Phillips Jr., G.N.(2009) Proteins 76: 477-483
- PubMed: 19241471
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.22362
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2BE4 - PubMed Abstract:
Many essential physiological processes are regulated by the modulation of calcium concentration in the cell. The EF-hand proteins represent a superfamily of calcium-binding proteins involved in calcium signaling and homeostasis. Secretagogin is a hexa-EF-hand protein that is highly expressed in pancreatic islet of Langerhans and neuroendocrine cells and may play a role in the trafficking of secretory granules. We present the X-ray structure of Danio rerio secretagogin, which is 73% identical to human secretagogin, in calcium-free form at 2.1-A resolution. Secretagogin consists of the three globular domains each of which contains a pair of EF-hand motifs. The domains are arranged into a V-shaped molecule with a distinct groove formed at the interface of the domains. Comparison of the secretagogin structure with the solution structure of calcium-loaded calbindin D(28K) revealed a striking difference in the spatial arrangement of their domains, which involves approximately 180 degrees rotation of the first globular domain with respect to the module formed by the remaining domains.
- Department of Biochemistry, Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, 53706-1544, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: