Disulfide Bridges in the Mesophilic Triosephosphate Isomerase from Giardia lamblia Are Related to Oligomerization and Activity
Reyes-Vivas, H., Diaz, A., Peon, J., Mendoza-Hernandez, G., Hernandez-Alcantara, G., De la Mora-De la Mora, I., Enriquez-Flores, S., Dominguez-Ramirez, L., Lopez-Velazquez, G.(2007) J Mol Biol 365: 752-763
- PubMed: 17095008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.10.053
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
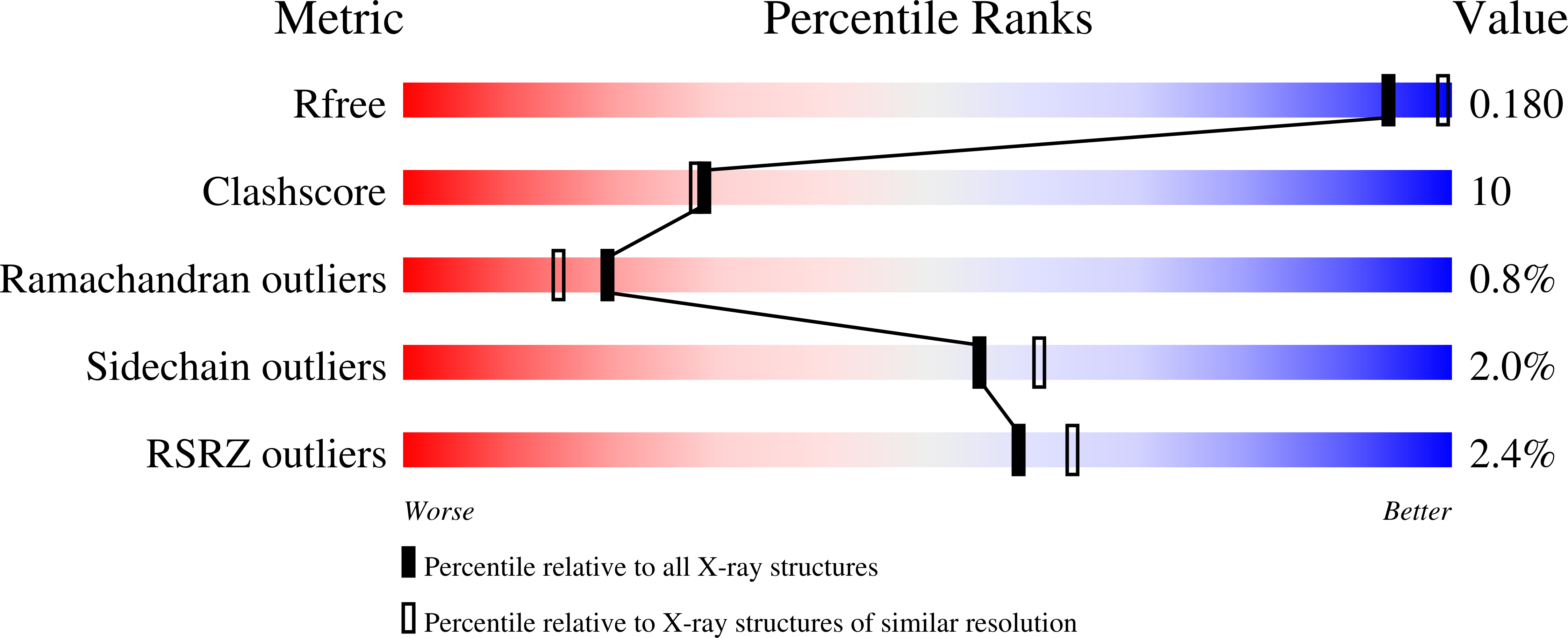
2DP3 - PubMed Abstract:
Triosephosphate isomerase from the mesophile Giardia lamblia (GlTIM) is the only known TIM with natural disulfide bridges. We previously found that oxidized and reduced thiol states of GlTIM are involved in the interconversion between native dimers and higher oligomeric species, and in the regulation of enzymatic activity. Here, we found that trophozoites and cysts have different oligomeric species of GlTIM and complexes of GlTIM with other proteins. Our data indicate that the internal milieu of G. lamblia is favorable for the formation of disulfide bonds. Enzyme mutants of the three most solvent exposed Cys of GlTIM (C202A, C222A, and C228A) were prepared to ascertain their contribution to oligomerization and activity. The data show that the establishment of a disulfide bridge between two C202 of two dimeric GlTIMs accounts for multimerization. In addition, we found that the establishment of an intramonomeric disulfide bond between C222 and C228 abolishes catalysis. Multimerization and inactivation are both reversed by reducing conditions. The 3D structure of the C202A GlTIM was solved at 2.1 A resolution, showing that the environment of the C202 is prone to hydrophobic interactions. Molecular dynamics of an in silico model of GlTIM when the intramonomeric disulfide bond is formed, showed that S216 is displaced 4.6 A from its original position, causing loss of hydrogen bonds with residues of the active-site loop. This suggests that this change perturb the conformational state that aligns the catalytic center with the substrate, inducing enzyme inactivation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratorio de Bioquimica Genetica, Instituto Nacional de Pediatria, 04530 Mexico, D.F.