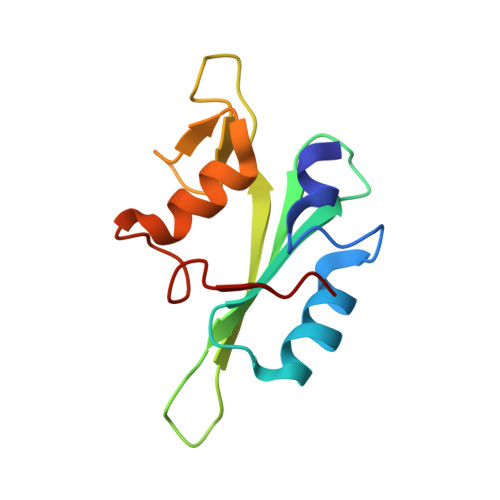
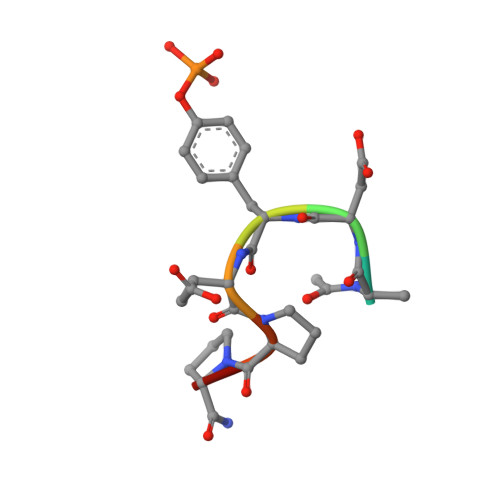
Molecular Details of Itk Activation by Prolyl Isomerization and Phospholigand Binding: The NMR Structure of the Itk SH2 Domain Bound to a Phosphopeptide.
Pletneva, E.V., Sundd, M., Fulton, D.B., Andreotti, A.H.(2006) J Mol Biology 357: 550-561
- PubMed: 16436281
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2005.12.073
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2ETZ, 2EU0 - PubMed Abstract:
The Src homology 2 (SH2) domain of interleukin-2 tyrosine kinase (Itk) is a critical component of the regulatory apparatus controlling the activity of this immunologically important enzyme. To gain insight into the structural features associated with the activated form of Itk, we have solved the NMR structure of the SH2 domain bound to a phosphotyrosine-containing peptide (pY) and analyzed changes in trans-hydrogen bond scalar couplings ((3h)J(NC')) that result from pY binding. Isomerization of a single prolyl imide bond in this domain is responsible for simultaneous existence of two distinct SH2 conformers. Prolyl isomerization directs ligand recognition: the trans conformer preferentially binds pY. The structure of the SH2/pY complex provides insight into the ligand specificity; the BG loop in the ligand-free trans SH2 conformer is pre-arranged for optimal contacts with the pY+3 residue of the ligand. Analysis of (3h)J(NC') couplings arising from hydrogen bonds has revealed propagation of structural changes from the pY binding pocket to the CD loop containing conformationally heterogeneous proline as well as to the alphaB helix, on the opposite site of the domain. These findings offer a structural framework for understanding the roles of prolyl isomerization and pY binding in Itk regulation.
- Department of Biochemistry, Biophysics and Molecular Biology, Iowa State University, Ames, IA 50011, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: