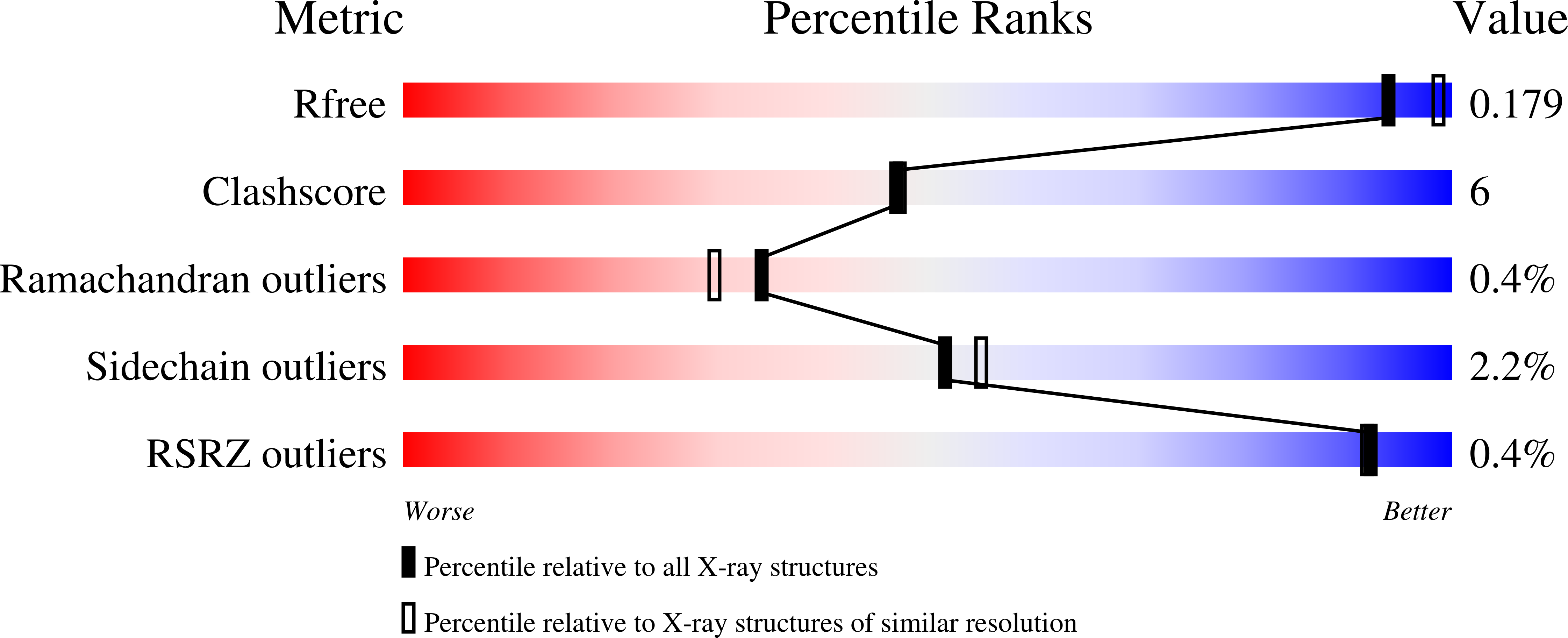
Structure of the Y94F mutant of Escherichia coli thymidylate synthase.
Roberts, S.A., Hyatt, D.C., Honts, J.E., Changchien, L., Maley, G.F., Maley, F., Montfort, W.R.(2006) Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 62: 840-843
- PubMed: 16946460
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1744309106029691
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2FTN, 2FTO - PubMed Abstract:
Tyr94 of Escherichia coli thymidylate synthase is thought to be involved, either directly or by activation of a water molecule, in the abstraction of a proton from C5 of the 2'-deoxyuridine 5'-monophosphate (dUMP) substrate. Mutation of Tyr94 leads to a 400-fold loss in catalytic activity. The structure of the Y94F mutant has been determined in the native state and as a ternary complex with thymidine 5'-monophosphate (dTMP) and 10-propargyl 5,8-dideazafolate (PDDF). There are no structural changes ascribable to the mutation other than loss of a water molecule hydrogen bonded to the tyrosine OH, which is consistent with a catalytic role for the phenolic OH.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721, USA.