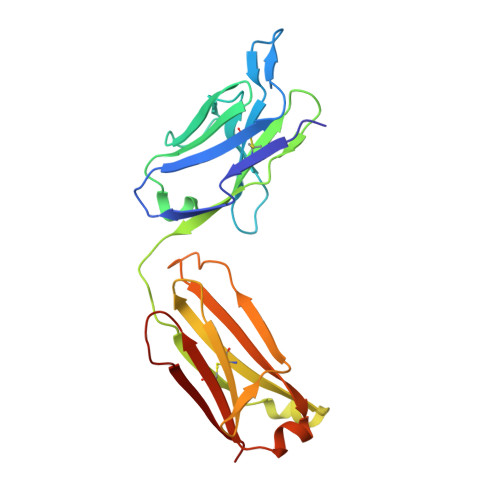
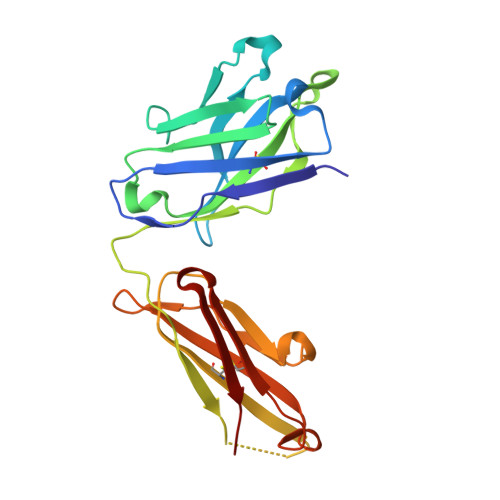
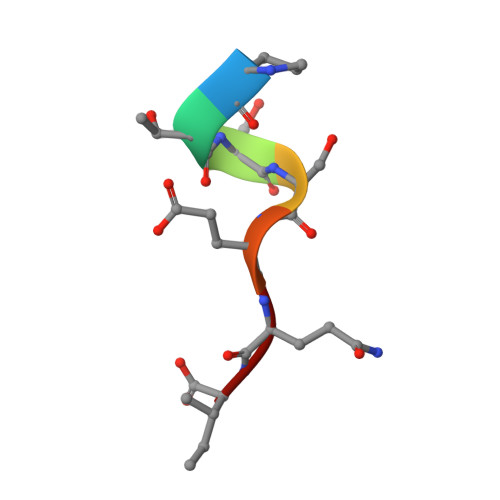
Elucidation of some Bax conformational changes through crystallization of an antibody-peptide complex.
Peyerl, F.W., Dai, S., Murphy, G.A., Crawford, F., White, J., Marrack, P., Kappler, J.W.(2007) Cell Death Differ 14: 447-452
- PubMed: 16946732
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4402025
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2G5B - PubMed Abstract:
The Bcl-2 family member Bax plays a critical role in apoptosis. In healthy resting cells, Bax resides in the cytoplasm and loosely attached to the mitochondrial membrane. Apoptotic stimuli induce Bax activation, which is characterized by translocation and multimerization on the mitochondrial membrane surface resulting in exposure of an amino terminal epitope recognized by the monoclonal antibody 6A7. To understand the structural changes that occur during Bax activation, we determined the crystal structure of a Bax peptide bound to the 6A7 Fab fragment to a resolution of 2.3 A. The structure reveals the conformation of the 6A7 peptide epitope on Bax in the activated form and elucidates the extensive structural changes that Bax must undergo during the conversion from its native to its activated conformation.
- 1Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Integrated Department of Immunology, Zuckerman Family/Canyon Ranch Crystallography Laboratory, National Jewish Medical and Research Center, Denver, CO 80206, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: