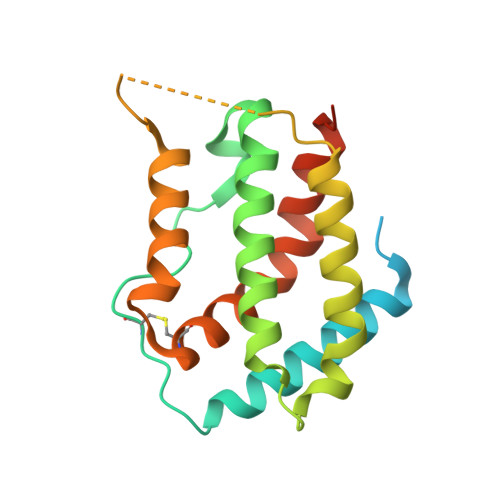
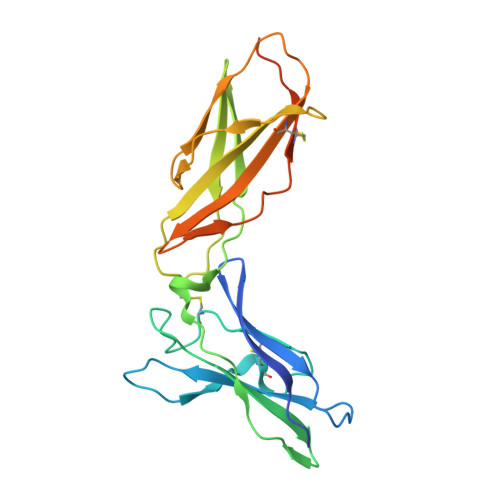
Crystal structure of the complex of human interferon-lambda1 with its high affinity receptor interferon-lambdaR1.
Miknis, Z.J., Magracheva, E., Li, W., Zdanov, A., Kotenko, S.V., Wlodawer, A.(2010) J Mol Biology 404: 650-664
- PubMed: 20934432
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.09.068
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3OG4, 3OG6 - PubMed Abstract:
Interferon (IFN)-λ1 [also known as interleukin (IL)-29] belongs to the recently discovered group of type III IFNs. All type III IFNs initiate signaling processes through formation of specific heterodimeric receptor complexes consisting of IFN-λR1 and IL-10R2. We have determined the structure of human IFN-λ1 complexed with human IFN-λR1, a receptor unique to type III IFNs. The overall structure of IFN-λ1 is topologically similar to the structure of IL-10 and other members of the IL-10 family of cytokines. IFN-λR1 consists of two distinct domains having fibronectin type III topology. The ligand-receptor interface includes helix A, loop AB, and helix F on the IFN site, as well as loops primarily from the N-terminal domain and inter-domain hinge region of IFN-λR1. Composition and architecture of the interface that includes only a few direct hydrogen bonds support an idea that long-range ionic interactions between ligand and receptor govern the process of initial recognition of the molecules while hydrophobic interactions finalize it.
- Macromolecular Crystallography Laboratory, NCI-Frederick, Frederick, MD 21702, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: