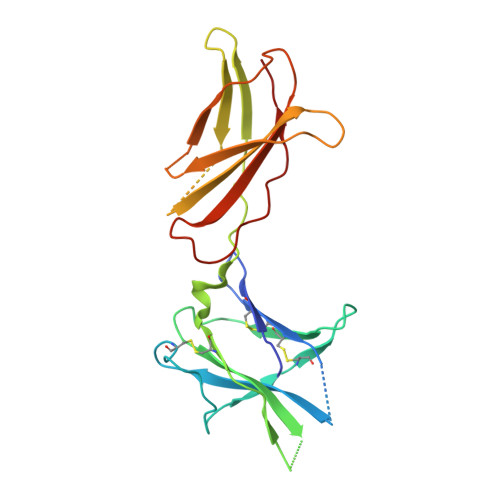
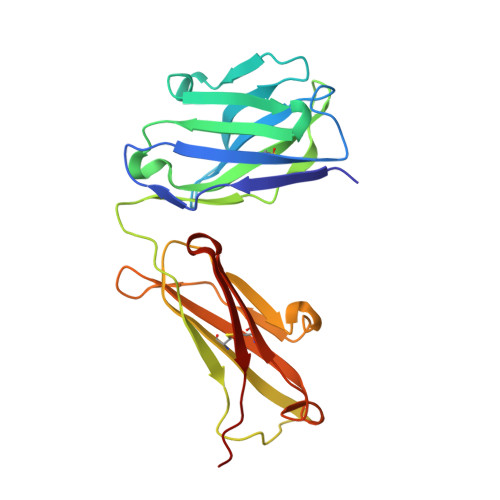
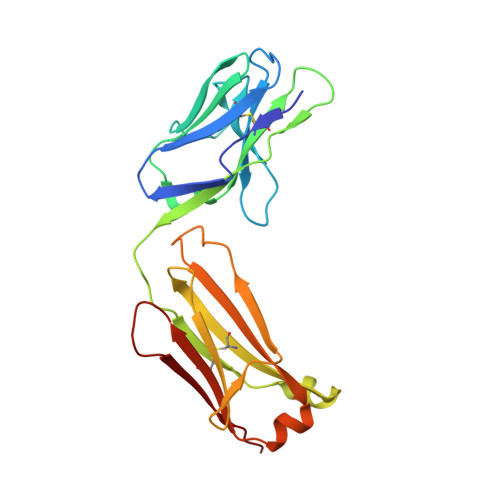
Structure of the human obesity receptor leptin-binding domain reveals the mechanism of leptin antagonism by a monoclonal antibody.
Carpenter, B., Hemsworth, G.R., Wu, Z., Maamra, M., Strasburger, C.J., Ross, R.J., Artymiuk, P.J.(2012) Structure 20: 487-497
- PubMed: 22405007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2012.01.019
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3V6O, 3VG0 - PubMed Abstract:
Leptin regulates energy homeostasis, fertility, and the immune system, making it an important drug target. However, due to a complete lack of structural data for the obesity receptor (ObR), leptin's mechanism of receptor activation remains poorly understood. We have crystallized the Fab fragment of a leptin-blocking monoclonal antibody (9F8), both in its uncomplexed state and bound to the leptin-binding domain (LBD) of human ObR. We describe the structure of the LBD-9F8 Fab complex and the conformational changes in 9F8 associated with LBD binding. A molecular model of the putative leptin-LBD complex reveals that 9F8 Fab blocks leptin binding through only a small (10%) overlap in their binding sites, and that leptin binding is likely to involve an induced fit mechanism. This crystal structure of the leptin-binding domain of the obesity receptor will facilitate the design of therapeutics to modulate leptin signaling.
- Academic Unit of Diabetes, Endocrinology and Reproduction, Department of Human Metabolism, University of Sheffield, Sheffield S10 2JF, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: