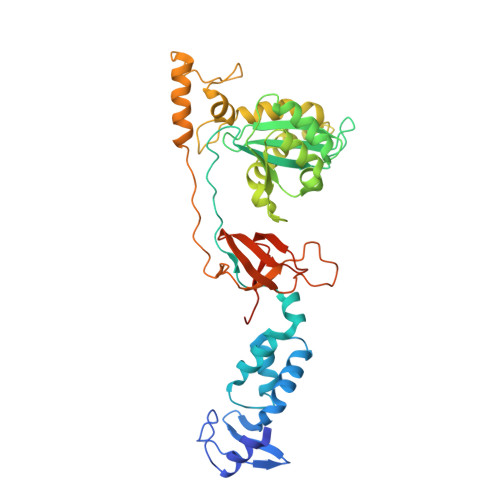
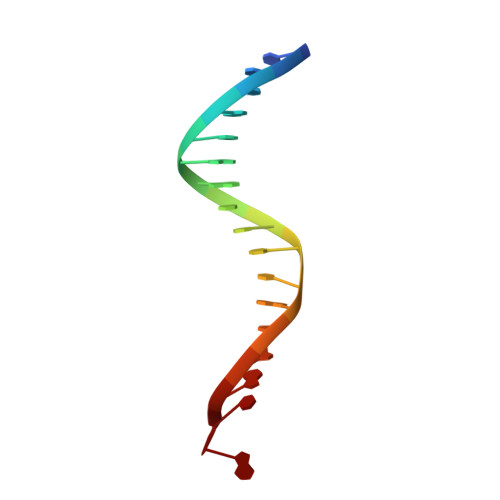
Activities, Crystal Structures and Molecular Dynamics of Dihydro-1H-Isoindole Derivatives, Inhibitors of HIV-1 Integrase.
Metifiot, M., Maddali, K., Johnson, B.C., Hare, S., Smith, S.J., Zhao, X.Z., Marchand, C., Burke, T.R., Hughes, S.H., Cherepanov, P., Pommier, Y.(2013) ACS Chem Biol 8: 209
- PubMed: 23075516
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/cb300471n
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4BDY, 4BDZ, 4BE0, 4BE1, 4BE2 - PubMed Abstract:
On the basis of a series of lactam and phthalimide derivatives that inhibit HIV-1 integrase, we developed a new molecule, XZ-259, with biochemical and antiviral activities comparable to raltegravir. We determined the crystal structures of XZ-259 and four other derivatives in complex with the prototype foamy virus intasome. The compounds bind at the integrase-Mg(2+)-DNA interface of the integrase active site. In biochemical and antiviral assays, XZ-259 inhibits raltegravir-resistant HIV-1 integrases harboring the Y143R mutation. Molecular modeling is also presented suggesting that XZ-259 can bind in the HIV-1 intasome with its dimethyl sulfonamide group adopting two opposite orientations. Molecular dynamics analyses of the HIV-1 intasome highlight the importance of the viral DNA in drug potency.
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health , 37 Convent Drive, Bethesda, Maryland 20892, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: