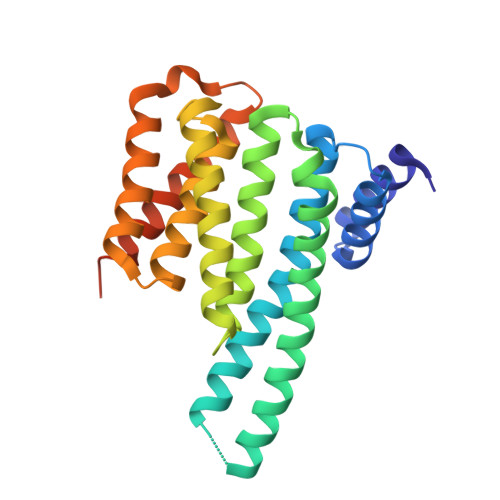
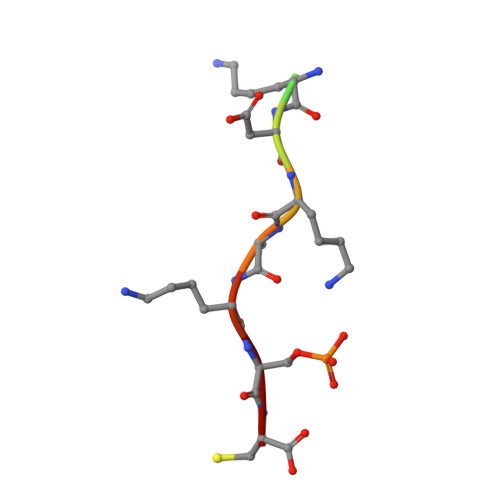
14-3-3 Proteins Interact with a Hybrid Prenyl-Phosphorylation Motif to Inhibit G Proteins.
Riou, P., Kjaer, S., Garg, R., Purkiss, A., George, R., Cain, R.J., Bineva, G., Reymond, N., Mccoll, B., Thompson, A.J., O'Reilly, N., Mcdonald, N.Q., Parker, P.J., Ridley, A.J.(2013) Cell 153: 640
- PubMed: 23622247
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.03.044
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4BG6 - PubMed Abstract:
Signaling through G proteins normally involves conformational switching between GTP- and GDP-bound states. Several Rho GTPases are also regulated by RhoGDI binding and sequestering in the cytosol. Rnd proteins are atypical constitutively GTP-bound Rho proteins, whose regulation remains elusive. Here, we report a high-affinity 14-3-3-binding site at the C terminus of Rnd3 consisting of both the Cys241-farnesyl moiety and a Rho-associated coiled coil containing protein kinase (ROCK)-dependent Ser240 phosphorylation site. 14-3-3 binding to Rnd3 also involves phosphorylation of Ser218 by ROCK and/or Ser210 by protein kinase C (PKC). The crystal structure of a phosphorylated, farnesylated Rnd3 peptide with 14-3-3 reveals a hydrophobic groove in 14-3-3 proteins accommodating the farnesyl moiety. Functionally, 14-3-3 inhibits Rnd3-induced cell rounding by translocating it from the plasma membrane to the cytosol. Rnd1, Rnd2, and geranylgeranylated Rap1A interact similarly with 14-3-3. In contrast to the canonical GTP/GDP switch that regulates most Ras superfamily members, our results reveal an unprecedented mechanism for G protein inhibition by 14-3-3 proteins.
- Randall Division of Cell and Molecular Biophysics, New Hunt's House, King's College London, London, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: