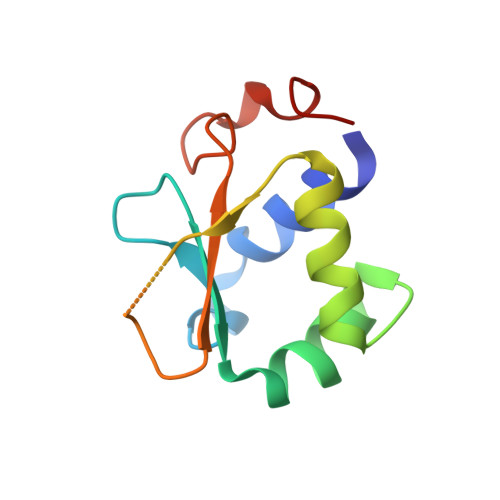
Structure of human heat-shock transcription factor 1 in complex with DNA.
Neudegger, T., Verghese, J., Hayer-Hartl, M., Hartl, F.U., Bracher, A.(2016) Nat Struct Mol Biol 23: 140-146
- PubMed: 26727489
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3149
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5D5U, 5D5V, 5D5W, 5D5X, 5D5Y, 5D5Z, 5D60 - PubMed Abstract:
Heat-shock transcription factor 1 (HSF1) has a central role in mediating the protective response to protein conformational stresses in eukaryotes. HSF1 consists of an N-terminal DNA-binding domain (DBD), a coiled-coil oligomerization domain, a regulatory domain and a transactivation domain. Upon stress, HSF1 trimerizes via its coiled-coil domain and binds to the promoters of heat shock protein-encoding genes. Here, we present cocrystal structures of the human HSF1 DBD in complex with cognate DNA. A comparative analysis of the HSF1 paralog Skn7 from Chaetomium thermophilum showed that single amino acid changes in the DBD can switch DNA binding specificity, thus revealing the structural basis for the interaction of HSF1 with cognate DNA. We used a crystal structure of the coiled-coil domain of C. thermophilum Skn7 to develop a model of the active human HSF1 trimer in which HSF1 embraces the heat-shock-element DNA.
- Department of Cellular Biochemistry, Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry, Martinsried, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: