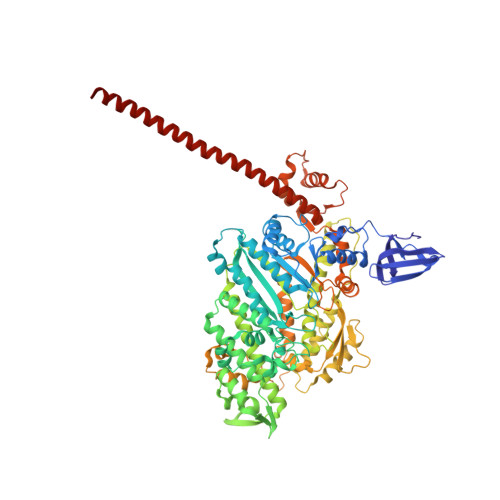
The myosin X motor is optimized for movement on actin bundles.
Ropars, V., Yang, Z., Isabet, T., Blanc, F., Zhou, K., Lin, T., Liu, X., Hissier, P., Samazan, F., Amigues, B., Yang, E.D., Park, H., Pylypenko, O., Cecchini, M., Sindelar, C.V., Sweeney, H.L., Houdusse, A.(2016) Nat Commun 7: 12456-12456
- PubMed: 27580874
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12456
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5HMO, 5HMP, 5I0H, 5I0I, 5KG8 - PubMed Abstract:
Myosin X has features not found in other myosins. Its structure must underlie its unique ability to generate filopodia, which are essential for neuritogenesis, wound healing, cancer metastasis and some pathogenic infections. By determining high-resolution structures of key components of this motor, and characterizing the in vitro behaviour of the native dimer, we identify the features that explain the myosin X dimer behaviour. Single-molecule studies demonstrate that a native myosin X dimer moves on actin bundles with higher velocities and takes larger steps than on single actin filaments. The largest steps on actin bundles are larger than previously reported for artificially dimerized myosin X constructs or any other myosin. Our model and kinetic data explain why these large steps and high velocities can only occur on bundled filaments. Thus, myosin X functions as an antiparallel dimer in cells with a unique geometry optimized for movement on actin bundles.
- Structural Motility, Institut Curie, PSL Research University, CNRS, UMR 144, F-75005 Paris, France.
Organizational Affiliation: