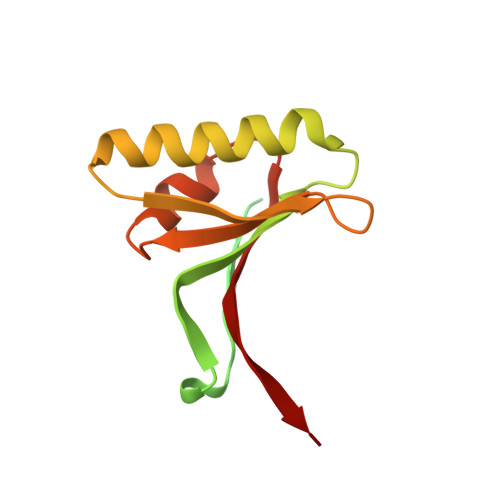
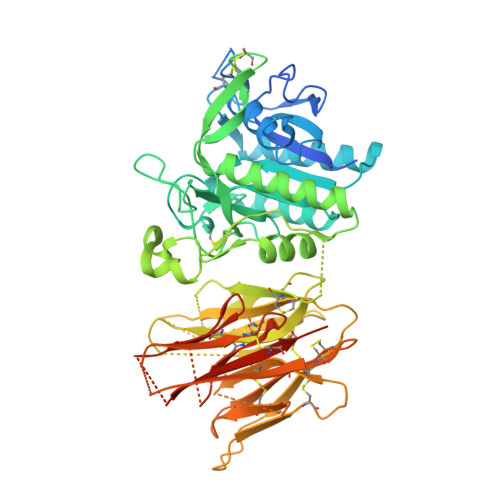
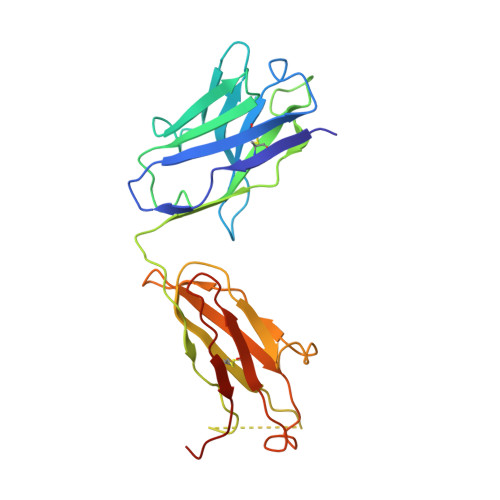
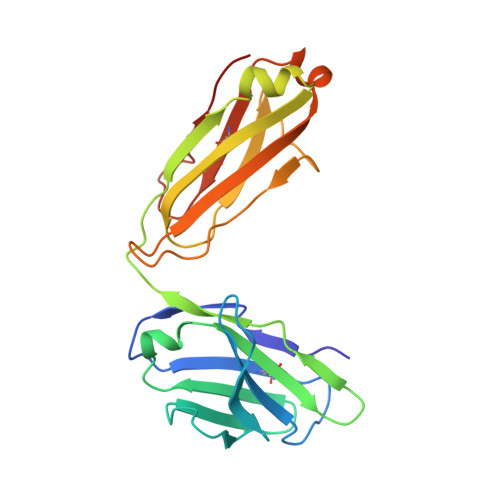
Discovery of a cryptic peptide-binding site on PCSK9 and design of antagonists.
Zhang, Y., Ultsch, M., Skelton, N.J., Burdick, D.J., Beresini, M.H., Li, W., Kong-Beltran, M., Peterson, A., Quinn, J., Chiu, C., Wu, Y., Shia, S., Moran, P., Di Lello, P., Eigenbrot, C., Kirchhofer, D.(2017) Nat Struct Mol Biol 24: 848-856
- PubMed: 28825733
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3453
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5VL7, 5VLA, 5VLH, 5VLK, 5VLL, 5VLP - PubMed Abstract:
Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) regulates plasma LDL cholesterol (LDL-c) levels by promoting the degradation of liver LDL receptors (LDLRs). Antibodies that inhibit PCSK9 binding to the EGF(A) domain of the LDLR are effective in lowering LDL-c. However, the discovery of small-molecule therapeutics is hampered by difficulty in targeting the relatively flat EGF(A)-binding site on PCSK9. Here we demonstrate that it is possible to target this site, based on the finding that the PCSK9 P' helix displays conformational flexibility. As a consequence, the vacated N-terminal groove of PCSK9, which is adjacent to the EGF(A)-binding site, is in fact accessible to small peptides. In phage-display experiments, the EGF(A)-mimicking peptide Pep2-8 was used as an anchor peptide for the attachment of an extension peptide library directed toward the groove site. Guided by structural information, we further engineered the identified groove-binding peptides into antagonists, which encroach on the EGF(A)-binding site and inhibit LDLR binding.
- Department of Early Discovery Biochemistry, Genentech, Inc., South San Francisco, California, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: