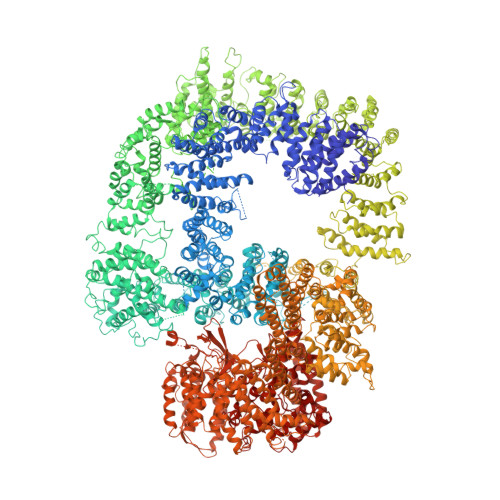
Cryo-EM structure of the DNA-PK holoenzyme.
Sharif, H., Li, Y., Dong, Y., Dong, L., Wang, W.L., Mao, Y., Wu, H.(2017) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114: 7367-7372
- PubMed: 28652322
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1707386114
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5W1R - PubMed Abstract:
DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) is a large protein complex central to the nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) DNA-repair pathway. It comprises the DNA-PK catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) and the heterodimer of DNA-binding proteins Ku70 and Ku80. Here, we report the cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of human DNA-PKcs at 4.4-Å resolution and the DNA-PK holoenzyme at 5.8-Å resolution. The DNA-PKcs structure contains three distinct segments: the N-terminal region with an arm and a bridge, the circular cradle, and the head that includes the kinase domain. Two perpendicular apertures exist in the structure, which are sufficiently large for the passage of dsDNA. The DNA-PK holoenzyme cryo-EM map reveals density for the C-terminal globular domain of Ku80 that interacts with the arm of DNA-PKcs. The Ku80-binding site is adjacent to the previously identified density for the DNA-binding region of the Ku70/Ku80 complex, suggesting concerted DNA interaction by DNA-PKcs and the Ku complex.
- Department of Biological Chemistry and Molecular Pharmacology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115.
Organizational Affiliation: