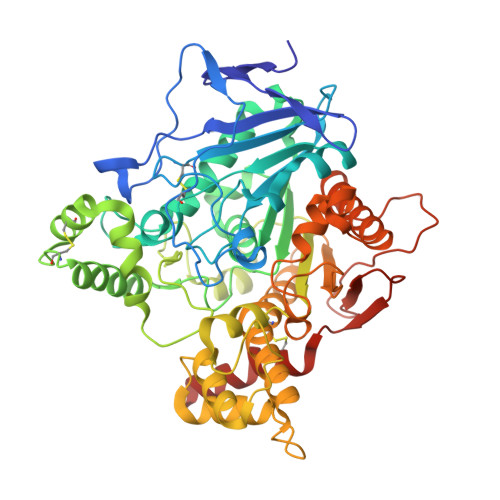
Novel multitarget-directed ligands targeting acetylcholinesterase and sigma1receptors as lead compounds for treatment of Alzheimer's disease: Synthesis, evaluation, and structural characterization of their complexes with acetylcholinesterase.
Lalut, J., Santoni, G., Karila, D., Lecoutey, C., Davis, A., Nachon, F., Silman, I., Sussman, J., Weik, M., Maurice, T., Dallemagne, P., Rochais, C.(2018) Eur J Med Chem 162: 234-248
- PubMed: 30447434
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.10.064
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6EZG, 6EZH - PubMed Abstract:
Pleiotropic intervention may be a requirement for effective limitation of the progression of multifactorial diseases such as Alzheimer's Disease. One approach to such intervention is to design a single chemical entity capable of acting on two or more targets of interest, which are accordingly known as Multi-Target Directed Ligands (MTDLs). We recently described donecopride, the first MTDL able to simultaneously inhibit acetylcholinesterase and act as an agonist of the 5-HT 4 receptor, which displays promising activities in vivo. Pharmacomodulation of donecopride allowed us to develop a novel series of indole derivatives possessing interesting in vitro activities toward AChE and the σ 1 receptor. The crystal structures of complexes of the most promising compounds with Torpedo californica AChE were solved in order to further understand their mode of inhibition.
- Centre d'Etudes et de Recherche sur le Médicament de Normandie, Normandie Univ, UNICAEN, CERMN, 14000, Caen, France.
Organizational Affiliation: