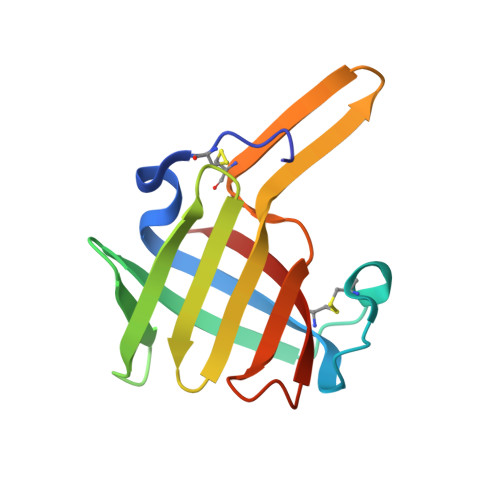
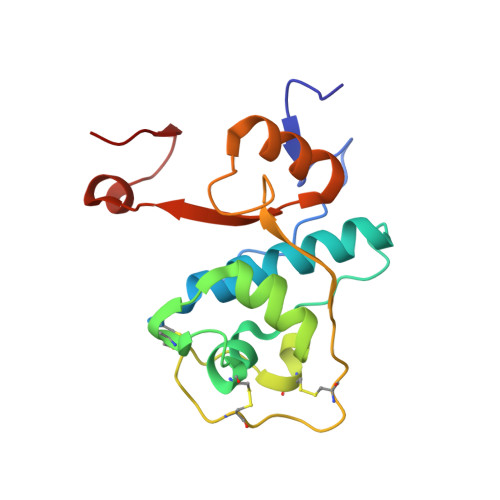
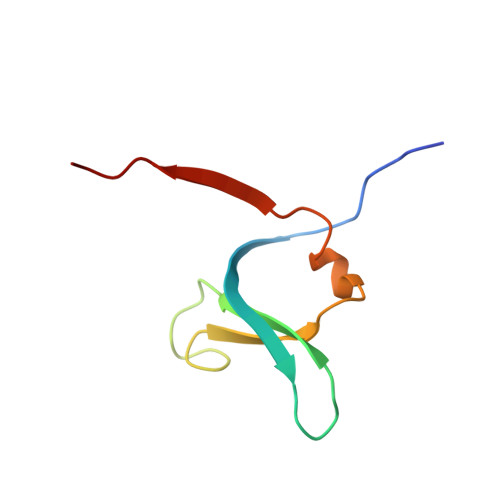
Structure-based design and in vivo anti-arthritic activity evaluation of a potent dipeptidyl cyclopropyl nitrile inhibitor of cathepsin C.
Korkmaz, B., Lesner, A., Wysocka, M., Gieldon, A., Hakansson, M., Gauthier, F., Logan, D.T., Jenne, D.E., Lauritzen, C., Pedersen, J.(2019) Biochem Pharmacol 164: 349-367
- PubMed: 30978322
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2019.04.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6IC5, 6IC6, 6IC7 - PubMed Abstract:
Cathepsin C (CatC) is a dipeptidyl-exopeptidase which activates neutrophil serine protease precursors (elastase, proteinase 3, cathepsin G and NSP4) by removing their N-terminal propeptide in bone marrow cells at the promyelocytic stage of neutrophil differentiation. The resulting active proteases are implicated in chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Hence, inhibition of CatC represents a therapeutic strategy to suppress excessive protease activities in various neutrophil mediated diseases. We designed and synthesized a series of dipeptidyl cyclopropyl nitrile compounds as putative CatC inhibitors. One compound, IcatC XPZ-01 ((S)-2-amino-N-((1R,2R)-1-cyano-2-(4'-(4-methylpiperazin-1-ylsulfonyl)biphenyl-4-yl)cyclopropyl)butanamide)) was identified as a potent inhibitor of both human and rodent CatC. In mice, pharmacokinetic studies revealed that IcatC XPZ-01 accumulated in the bone marrow reaching levels suitable for CatC inhibition. Subcutaneous administration of IcatC XPZ-01 in a monoclonal anti-collagen antibody induced mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis resulted in statistically significant anti-arthritic activity with persistent decrease in arthritis scores and paw thickness.
- INSERM, UMR 1100, "Centre d'Etude des Pathologies Respiratoires", 37032 Tours, France; Université de Tours, 37032 Tours, France. Electronic address: brice.korkmaz@inserm.fr.
Organizational Affiliation: