Activation of the alpha2Badrenoceptor by the sedative sympatholytic dexmedetomidine.
Yuan, D., Liu, Z., Kaindl, J., Maeda, S., Zhao, J., Sun, X., Xu, J., Gmeiner, P., Wang, H.W., Kobilka, B.K.(2020) Nat Chem Biol 16: 507-512
- PubMed: 32152538
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-020-0492-2
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6K41, 6K42 - PubMed Abstract:
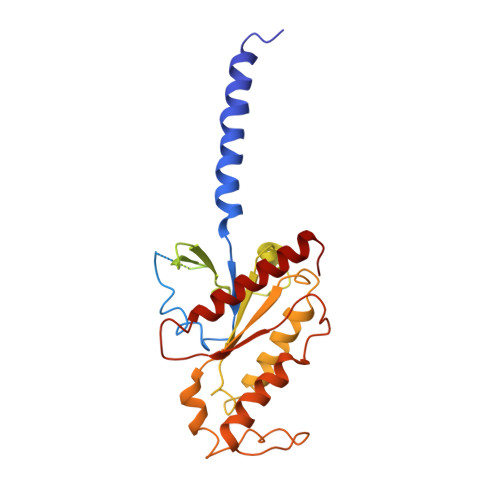
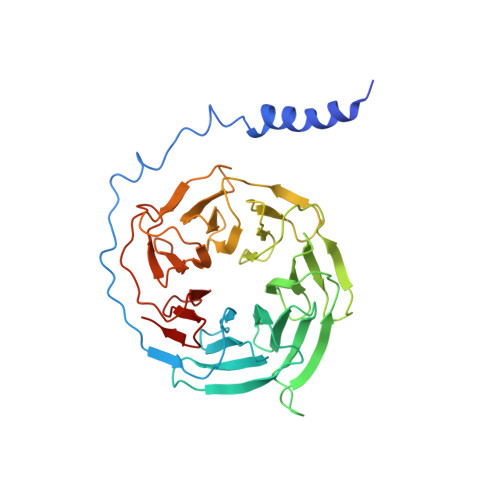
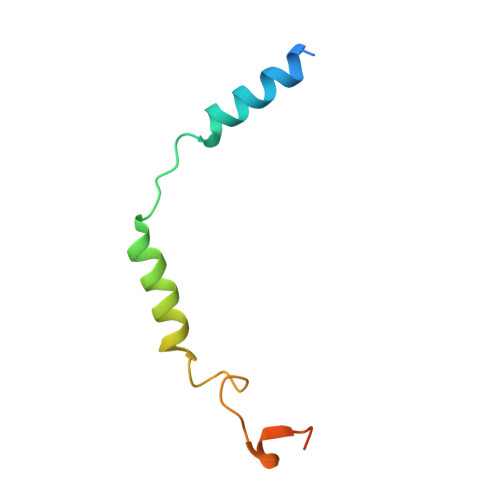
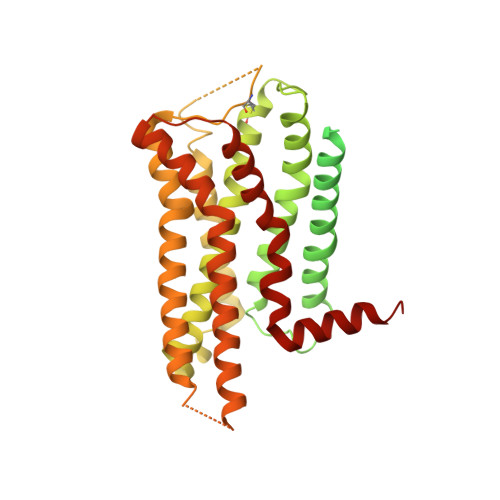
The α 2 adrenergic receptors (α 2 ARs) are G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that respond to adrenaline and noradrenaline and couple to the Gi/o family of G proteins. α 2 ARs play important roles in regulating the sympathetic nervous system. Dexmedetomidine is a highly selective α 2 AR agonist used in post-operative patients as an anxiety-reducing, sedative medicine that decreases the requirement for opioids. As is typical for selective αAR agonists, dexmedetomidine consists of an imidazole ring and a substituted benzene moiety lacking polar groups, which is in contrast to βAR-selective agonists, which share an ethanolamine group and an aromatic system with polar, hydrogen-bonding substituents. To better understand the structural basis for the selectivity and efficacy of adrenergic agonists, we determined the structure of the α 2B AR in complex with dexmedetomidine and Go at a resolution of 2.9 Å by single-particle cryo-EM. The structure reveals the mechanism of α 2 AR-selective activation and provides insights into Gi/o coupling specificity.
- Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Structural Biology, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China.
Organizational Affiliation: