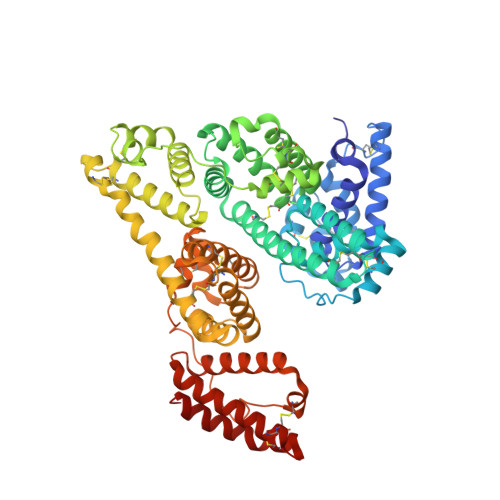
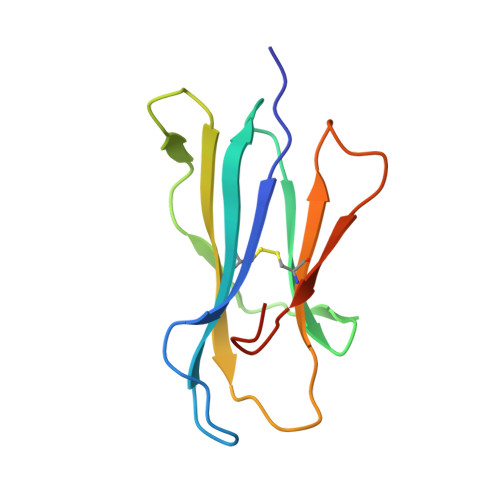
Identification of Binding Sites on Human Serum Albumin for Somapacitan, a Long-Acting Growth Hormone Derivative.
Johansson, E., Nielsen, A.D., Demuth, H., Wiberg, C., Schjodt, C.B., Huang, T., Chen, J., Jensen, S., Petersen, J., Thygesen, P.(2020) Biochemistry 59: 1410-1419
- PubMed: 32208682
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00019
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6QIO, 6QIP - PubMed Abstract:
Somapacitan, a human growth hormone derivative that binds reversibly to albumin, was investigated for human serum albumin (HSA) and HSA domain binding. Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) binding profiles showed high-affinity binding (∼100-1000 nM) of one somapacitan molecule and low-affinity binding (∼1000-10000 nM) of one to two somapacitan molecules to HSA. The high-affinity site was identified in HSA domain III using size exclusion chromatography (SEC) and ITC. SEC studies showed that the neonatal Fc receptor shields one binding site for somapacitan, indicating its position in domain III. A crystal structure of somapacitan in complex with HSA optimized for neonatal Fc receptor binding, having four amino acid residue replacements, identified a low-affinity site in fatty acid-binding site 6 (domain II). Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) showed these replacements affect the kinetics of the high-affinity binding site. Furthermore, small-angle X-ray scattering and SPR brace two somapacitan-binding sites on HSA.
- Novo Nordisk A/S, Novo Nordisk Park 1, DK-2760 Måløv, Denmark.
Organizational Affiliation: