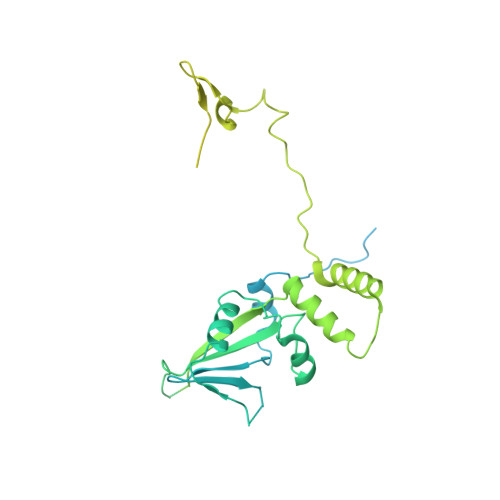
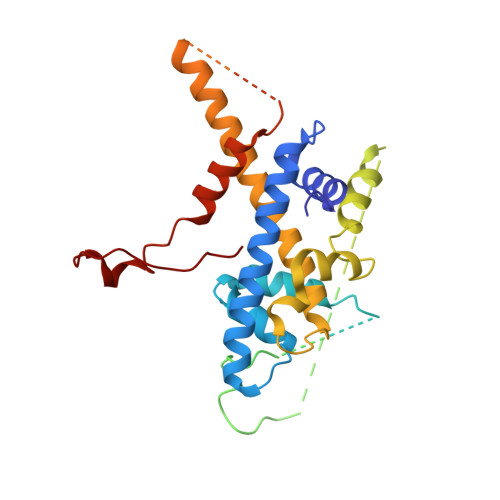
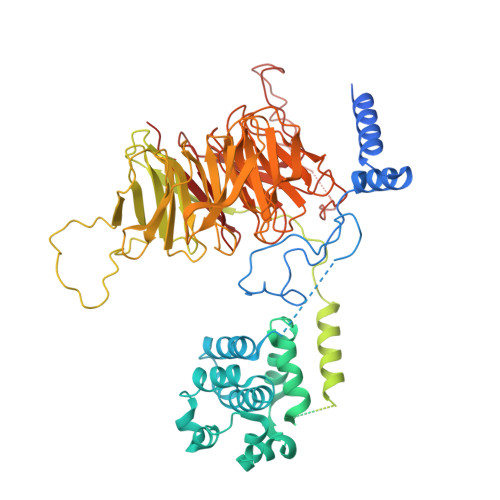
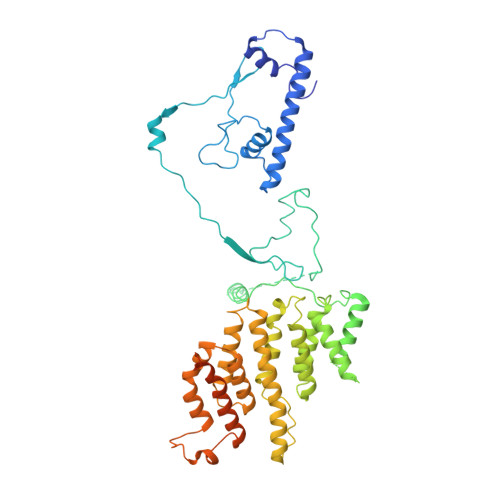
Structure of the transcription coactivator SAGA.
Wang, H., Dienemann, C., Stutzer, A., Urlaub, H., Cheung, A.C.M., Cramer, P.(2020) Nature 577: 717-720
- PubMed: 31969703
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-1933-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6T9I, 6T9J, 6T9K, 6T9L - PubMed Abstract:
Gene transcription by RNA polymerase II is regulated by activator proteins that recruit the coactivator complexes SAGA (Spt-Ada-Gcn5-acetyltransferase) 1,2 and transcription factor IID (TFIID) 2-4 . SAGA is required for all regulated transcription 5 and is conserved among eukaryotes 6 . SAGA contains four modules 7-9 : the activator-binding Tra1 module, the core module, the histone acetyltransferase (HAT) module and the histone deubiquitination (DUB) module. Previous studies provided partial structures 10-14 , but the structure of the central core module is unknown. Here we present the cryo-electron microscopy structure of SAGA from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and resolve the core module at 3.3 Å resolution. The core module consists of subunits Taf5, Sgf73 and Spt20, and a histone octamer-like fold. The octamer-like fold comprises the heterodimers Taf6-Taf9, Taf10-Spt7 and Taf12-Ada1, and two histone-fold domains in Spt3. Spt3 and the adjacent subunit Spt8 interact with the TATA box-binding protein (TBP) 2,7,15-17 . The octamer-like fold and its TBP-interacting region are similar in TFIID, whereas Taf5 and the Taf6 HEAT domain adopt distinct conformations. Taf12 and Spt20 form flexible connections to the Tra1 module, whereas Sgf73 tethers the DUB module. Binding of a nucleosome to SAGA displaces the HAT and DUB modules from the core-module surface, allowing the DUB module to bind one face of an ubiquitinated nucleosome.
- Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Department of Molecular Biology, Göttingen, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: