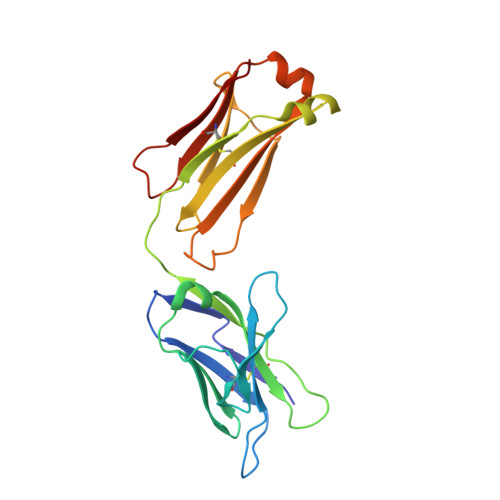
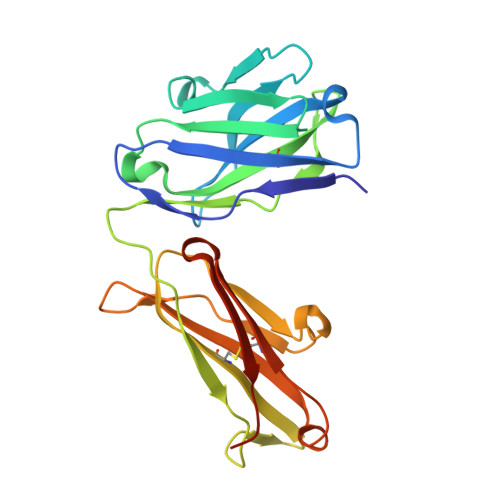
Structural Insights into How Protein Environments Tune the Spectroscopic Properties of a Noncanonical Amino Acid Fluorophore.
Henderson, J.N., Simmons, C.R., Fahmi, N.E., Jeffs, J.W., Borges, C.R., Mills, J.H.(2020) Biochemistry 59: 3401-3410
- PubMed: 32845612
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00474
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6BJZ, 6W4W, 6W5A, 6W9G - PubMed Abstract:
Genetically encoded fluorescent noncanonical amino acids (fNCAAs) could be used to develop novel fluorescent sensors of protein function. Previous efforts toward this goal have been limited by the lack of extensive physicochemical and structural characterizations of protein-based sensors containing fNCAAs. Here, we report the steady-state spectroscopic properties and first structural analyses of an fNCAA-containing Fab fragment of the 5c8 antibody, which binds human CD40L. A previously reported 5c8 variant in which the light chain residue Ile L 98 is replaced with the fNCAA l-(7-hydroxycoumarin-4-yl)ethylglycine (7-HCAA) exhibits a 1.7-fold increase in fluorescence upon antigen binding. Determination and comparison of the apparent p K a s of 7-HCAA in the unbound and bound forms indicate that the observed increase in fluorescence is not the result of perturbations in p K a . Crystal structures of the fNCAA-containing Fab in the apo and bound forms reveal interactions between the 7-HCAA side chain and surrounding residues that are disrupted upon antigen binding. This structural characterization not only provides insight into the manner in which protein environments can modulate the fluorescence properties of 7-HCAA but also could serve as a starting point for the rational design of new fluorescent protein-based reporters of protein function.
- The Biodesign Center for Molecular Design and Biomimetics, Arizona State University, Tempe, Arizona 85287, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: