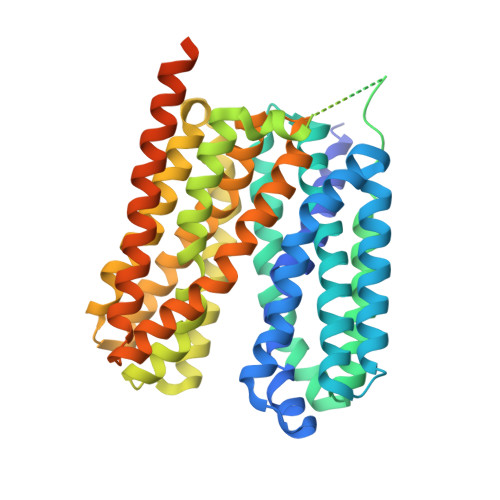
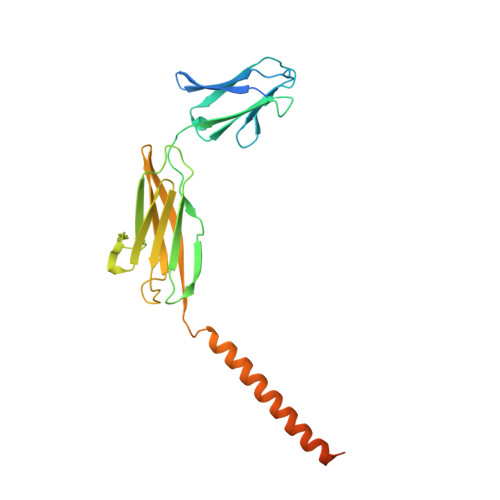
Structural basis of human monocarboxylate transporter 1 inhibition by anti-cancer drug candidates.
Wang, N., Jiang, X., Zhang, S., Zhu, A., Yuan, Y., Xu, H., Lei, J., Yan, C.(2021) Cell 184: 370
- PubMed: 33333023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.043
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6LYY, 6LZ0, 7CKO, 7CKR, 7DA5 - PubMed Abstract:
Proton-coupled monocarboxylate transporters MCT1-4 catalyze the transmembrane movement of metabolically essential monocarboxylates and have been targeted for cancer treatment because of their enhanced expression in various tumors. Here, we report five cryo-EM structures, at resolutions of 3.0-3.3 Å, of human MCT1 bound to lactate or inhibitors in the presence of Basigin-2, a single transmembrane segment (TM)-containing chaperon. MCT1 exhibits similar outward-open conformations when complexed with lactate or the inhibitors BAY-8002 and AZD3965. In the presence of the inhibitor 7ACC2 or with the neutralization of the proton-coupling residue Asp309 by Asn, similar inward-open structures were captured. Complemented by structural-guided biochemical analyses, our studies reveal the substrate binding and transport mechanism of MCTs, elucidate the mode of action of three anti-cancer drug candidates, and identify the determinants for subtype-specific sensitivities to AZD3965 by MCT1 and MCT4. These findings lay out an important framework for structure-guided drug discovery targeting MCTs.
- State Key Laboratory of Membrane Biology, Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Structural Biology, Tsinghua-Peking Center for Life Sciences, School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China.
Organizational Affiliation: