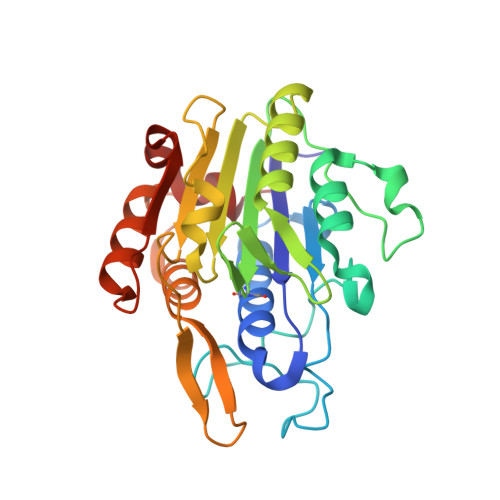
The Peptide Ligase Activity of Human Legumain Depends on Fold Stabilization and Balanced Substrate Affinities.
Dall, E., Stanojlovic, V., Demir, F., Briza, P., Dahms, S.O., Huesgen, P.F., Cabrele, C., Brandstetter, H.(2021) ACS Catal 11: 11885-11896
- PubMed: 34621593
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.1c02057
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7O50 - PubMed Abstract:
Protein modification by enzymatic breaking and forming of peptide bonds significantly expands the repertoire of genetically encoded protein sequences. The dual protease-ligase legumain exerts the two opposing activities within a single protein scaffold. Primarily localized to the endolysosomal system, legumain represents a key enzyme in the generation of antigenic peptides for subsequent presentation on the MHCII complex. Here we show that human legumain catalyzes the ligation and cyclization of linear peptides at near-neutral pH conditions, where legumain is intrinsically unstable. Conformational stabilization significantly enhanced legumain's ligase activity, which further benefited from engineering the prime substrate recognition sites for improved affinity. Additionally, we provide evidence that specific legumain activation states allow for differential regulation of its activities. Together these results set the basis for engineering legumain proteases and ligases with applications in biotechnology and drug development.
- Department of Biosciences, University of Salzburg, 5020 Salzburg, Austria.
Organizational Affiliation: