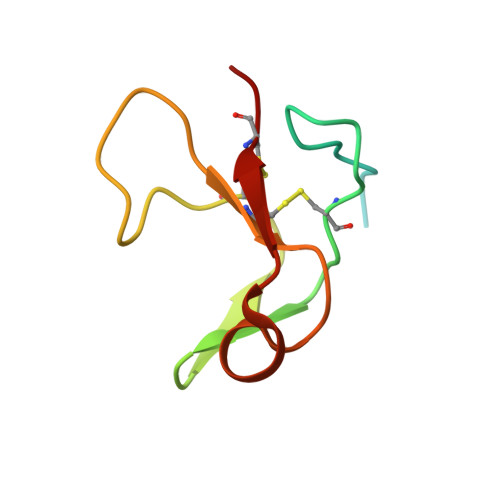
Crystal structure of coagulation factor XII N-terminal domains 1-5.
Saleem, M., Li, C., Kaira, B.G., Brown, A.K., Pathak, M., Najmudin, S., Cowieson, N., Dreveny, I., Wilson, C., Shamanaev, A., Gailani, D., Smith, S.A., Morrissey, J.H., Philippou, H., Emsley, J.(2025) Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 81: 380-393
- PubMed: 40576968
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798325005297
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7PRJ, 8OS5 - PubMed Abstract:
Factor XIIa (FXIIa) is generated from its zymogen factor XII (FXII) by contact with polyanions such as inorganic polyphosphates. FXIIa cleaves the substrates prekallikrein and factor XI, triggering inflammatory cascades and plasma coagulation. From the N-terminus, FXII has fibronectin type II (FnII), epidermal growth factor-1 (EGF1), fibronectin type I (FnI), EGF2 and kringle domains. The N-terminal domains of FXII mediate polyanion and Zn 2+ binding. To understand how ligand binding to polyanions and Zn 2+ is coordinated across multiple domains, we determined the crystal structure of recombinant FXII domains 1-5 (FXII HC5 ) to 3.4 Å resolution. A separate crystal structure of the isolated FXII FnII domain at 1.2 Å resolution revealed two bound Zn 2+ ions. In FXII HC5 a head-to-tail interaction is formed between the FnII and kringle domains, co-localizing the lysine-binding sites of the kringle domain and the cation-binding site of the FnII domain. Two FXII HC5 monomers interlock, burying a large surface area of 2067 Å 2 , such that two kringle domains point outwards separated by a distance of 20 Å. The polyanion-binding site in the EGF1 domain is localized onto a plane together with the FnII and FnI domains. Using native mass spectrometry, we detected a major FXII HC5 monomer peak and a minor dimer peak. Small-angle X-ray scattering and gel-filtration chromatography revealed the presence of monomers and dimers in solution. These FXII N-terminal domain structures provide a holistic framework to understand how the mosaic domain structure of FXII assembles diverse ligand-binding sites in three dimensions.
- Biodiscovery Institute, School of Pharmacy, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, United Kingdom.
Organizational Affiliation: