Targeting protein-ligand neosurfaces with a generalizable deep learning tool.
Marchand, A., Buckley, S., Schneuing, A., Pacesa, M., Elia, M., Gainza, P., Elizarova, E., Neeser, R.M., Lee, P.W., Reymond, L., Miao, Y., Scheller, L., Georgeon, S., Schmidt, J., Schwaller, P., Maerkl, S.J., Bronstein, M., Correia, B.E.(2025) Nature
- PubMed: 39814890
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-08435-4
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
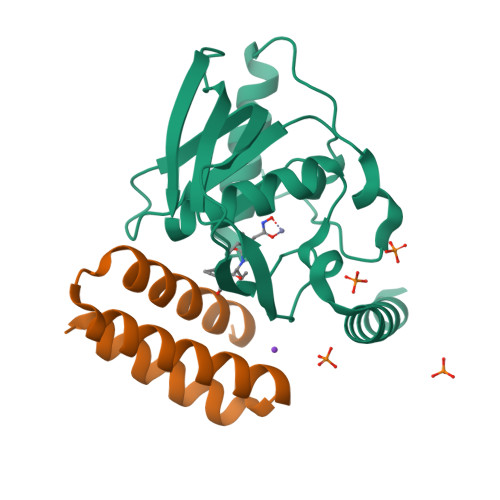
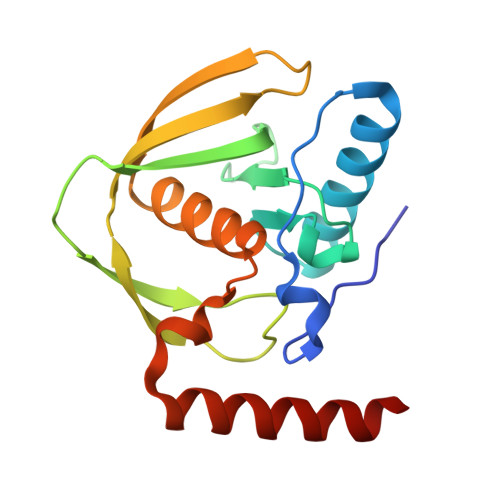
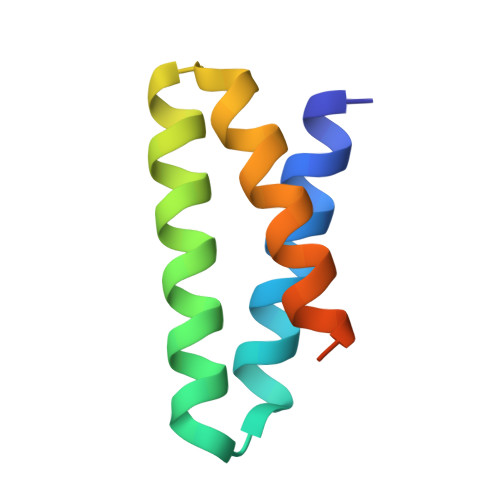
8S1X, 9FKD - PubMed Abstract:
Molecular recognition events between proteins drive biological processes in living systems 1 . However, higher levels of mechanistic regulation have emerged, in which protein-protein interactions are conditioned to small molecules 2-5 . Despite recent advances, computational tools for the design of new chemically induced protein interactions have remained a challenging task for the field 6,7 . Here we present a computational strategy for the design of proteins that target neosurfaces, that is, surfaces arising from protein-ligand complexes. To develop this strategy, we leveraged a geometric deep learning approach based on learned molecular surface representations 8,9 and experimentally validated binders against three drug-bound protein complexes: Bcl2-venetoclax, DB3-progesterone and PDF1-actinonin. All binders demonstrated high affinities and accurate specificities, as assessed by mutational and structural characterization. Remarkably, surface fingerprints previously trained only on proteins could be applied to neosurfaces induced by interactions with small molecules, providing a powerful demonstration of generalizability that is uncommon in other deep learning approaches. We anticipate that such designed chemically induced protein interactions will have the potential to expand the sensing repertoire and the assembly of new synthetic pathways in engineered cells for innovative drug-controlled cell-based therapies 10 .
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Protein Design and Immunoengineering, Institute of Bioengineering, Ecole polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland.