Crystal structure of histone deacetylase 6 complexed with (R)-lipoic acid, an essential cofactor in central carbon metabolism.
Watson, P.R., Stollmaier, J.G., Christianson, D.W.(2023) J Biol Chem 299: 105228-105228
- PubMed: 37703993
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105228
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
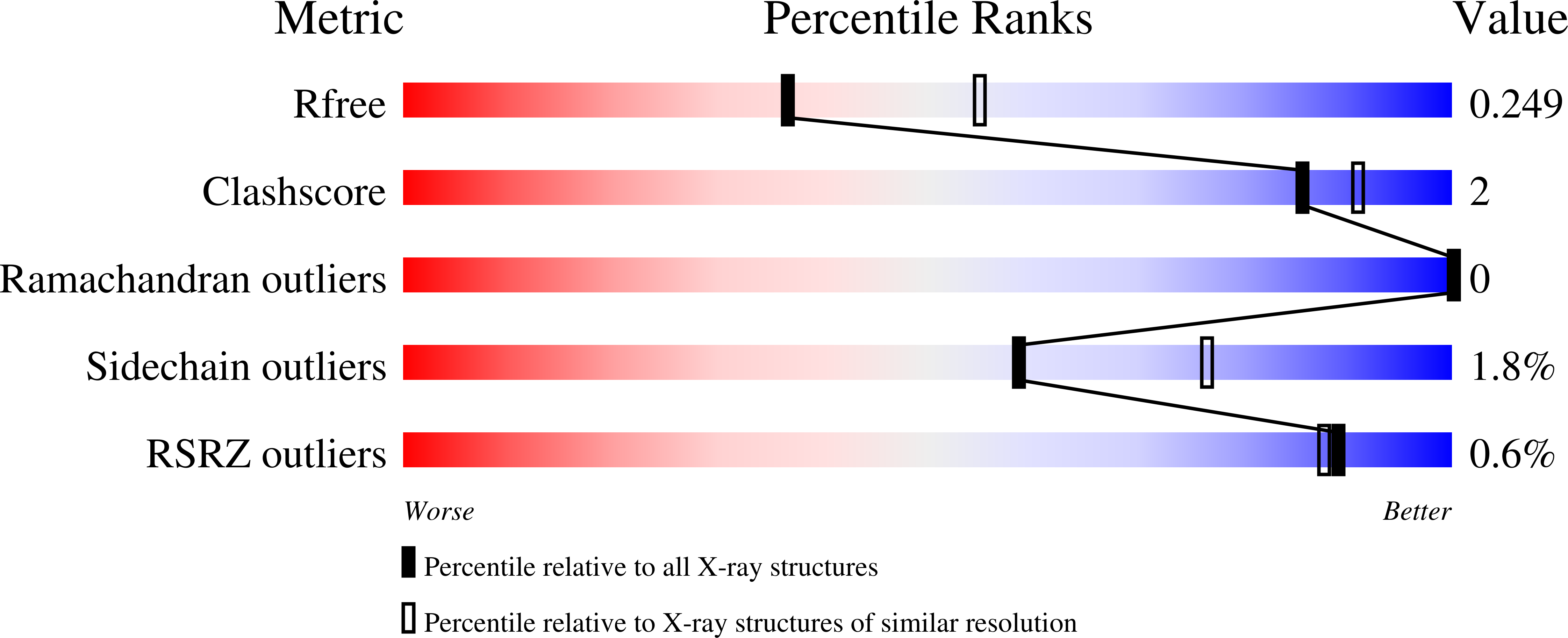
8TQ0 - PubMed Abstract:
The enzyme cofactor (R)-lipoic acid plays a critical role in central carbon metabolism due to its catalytic function in the generation of acetyl-CoA, which links glycolysis with the tricarboxylic acid cycle. This cofactor is also essential for the generation of succinyl CoA within the tricarboxylic acid cycle. However, the biological functions of (R)-lipoic acid extend beyond metabolism owing to its facile redox chemistry. Most recently, the reduced form of (R)-lipoic acid, (R)-dihydrolipoic acid, has been shown to inhibit histone deacetylases (HDACs) with selectivity for the inhibition of HDAC6. Here, we report the 2.4 Å-resolution X-ray crystal structure of the complex between (R)-dihydrolipoic acid and HDAC6 catalytic domain 2 from Danio rerio, and we report a dissociation constant (K D ) of 350 nM for this complex as determined by isothermal titration calorimetry. The crystal structure illuminates key affinity determinants in the enzyme active site, including thiolate-Zn 2+ coordination and S-π interactions in the F583-F643 aromatic crevice. This study provides the first visualization of the connection between HDAC function and the biological response to oxidative stress: the dithiol moiety of (R)-dihydrolipoic acid can serve as a redox-regulated pharmacophore capable of simultaneously targeting the catalytic Zn 2+ ion and the aromatic crevice in the active site of HDAC6.
Organizational Affiliation:
Roy and Diana Vagelos Laboratories, Department of Chemistry, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States.