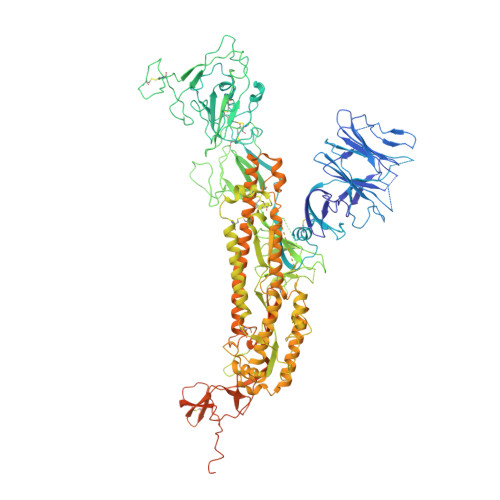
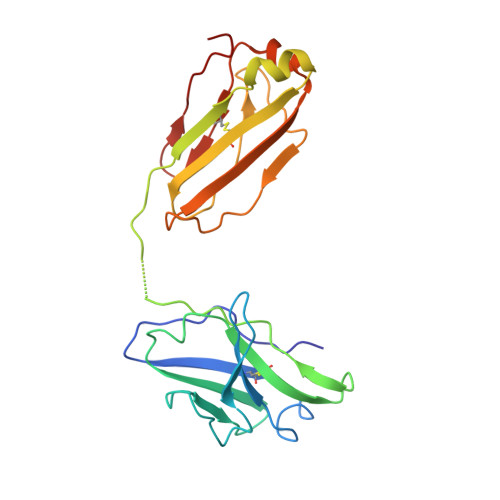
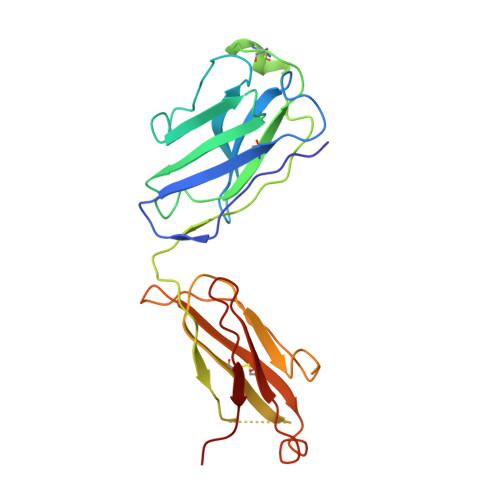
An unconventional VH1-2 antibody tolerates escape mutations and shows an antigenic hotspot on SARS-CoV-2 spike.
Liu, B., Niu, X., Deng, Y., Zhang, Z., Wang, Y., Gao, X., Liang, H., Li, Z., Wang, Q., Cheng, Y., Chen, Q., Huang, S., Pan, Y., Su, M., Lin, X., Niu, C., Chen, Y., Yang, W., Zhang, Y., Yan, Q., He, J., Zhao, J., Chen, L., Xiong, X.(2024) Cell Rep 43: 114265-114265
- PubMed: 38805396
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114265
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8ZBY, 8ZBZ, 8ZC0, 8ZC1, 8ZC2, 8ZC3, 8ZC4, 8ZC5, 8ZC6 - PubMed Abstract:
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike (S) protein continues to evolve antigenically, impacting antibody immunity. D1F6, an affinity-matured non-stereotypic VH1-2 antibody isolated from a patient infected with the SARS-CoV-2 ancestral strain, effectively neutralizes most Omicron variants tested, including XBB.1.5. We identify that D1F6 in the immunoglobulin G (IgG) form is able to overcome the effect of most Omicron mutations through its avidity-enhanced multivalent S-trimer binding. Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and biochemical analyses show that three simultaneous epitope mutations are generally needed to substantially disrupt the multivalent S-trimer binding by D1F6 IgG. Antigenic mutations at spike positions 346, 444, and 445, which appeared in the latest variants, have little effect on D1F6 binding individually. However, these mutations are able to act synergistically with earlier Omicron mutations to impair neutralization by affecting the interaction between D1F6 IgG and the S-trimer. These results provide insight into the mechanism by which accumulated antigenic mutations facilitate evasion of affinity-matured antibodies.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Disease, CAS Key Laboratory of Regenerative Biology, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Biocomputing, Guangzhou Institutes of Biomedicine and Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, China.