Canavalia bonariensis lectin: Molecular bases of glycoconjugates interaction and antiglioma potential.
Cavada, B.S., Silva, M.T.L., Osterne, V.J.S., Pinto-Junior, V.R., Nascimento, A.P.M., Wolin, I.A.V., Heinrich, I.A., Nobre, C.A.S., Moreira, C.G., Lossio, C.F., Rocha, C.R.C., Martins, J.L., Nascimento, K.S., Leal, R.B.(2018) Int J Biol Macromol 106: 369-378
- PubMed: 28803976
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.023
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5U3E - PubMed Abstract:
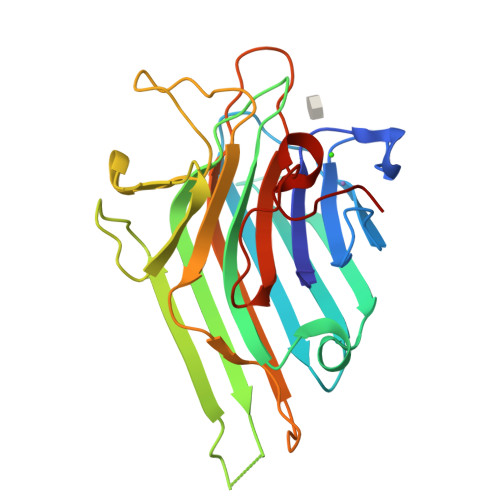
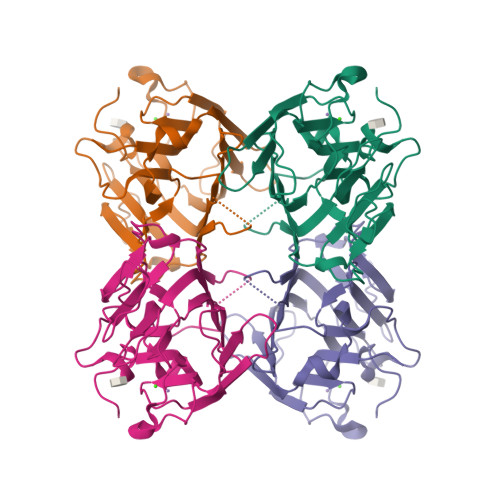
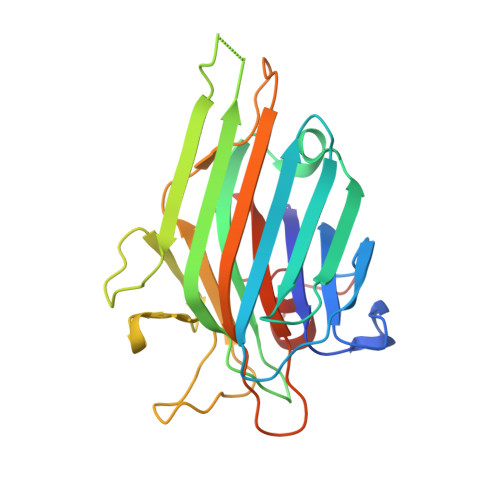
CaBo is a mannose/glucose-specific lectin purified from seeds of Canavalia bonariensis. In the present work, we report the CaBo crystal structure determined to atomic resolution in the presence of X-man, a specific ligand. Similar to the structural characteristics of other legume lectins, CaBo presented the jellyroll motif, a metal binding site occupied by calcium and manganese ions close to the carbohydrate-recognition domain (CRD). In vitro test of CaBo cytotoxicity against glioma cells demonstrated its ability to decrease the cellular viability and migration by induction of autophagy and cell death. Molecular docking simulations corroborate previous data indicating that the lectin's biological activities occur mostly through interactions with glycoproteins since the lectin interacted favorably with several N-glycans, especially those of the high-mannose type. Together, these results suggest that CaBo interacts with glycosylated cell targets and elicits a remarkable antiglioma activity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Universidade Federal do Ceará, Fortaleza, Ceará, Brazil. Electronic address: bscavada@ufc.br.