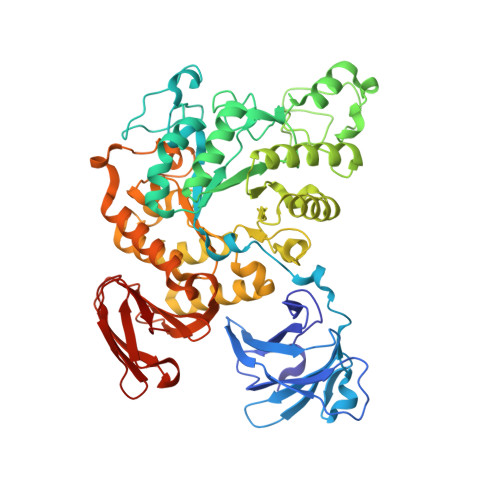
Crystal structures and structural comparison of Thermoactinomyces vulgaris R-47 alpha-amylase 1 (TVAI) at 1.6 A resolution and alpha-amylase 2 (TVAII) at 2.3 A resolution.
Kamitori, S., Abe, A., Ohtaki, A., Kaji, A., Tonozuka, T., Sakano, Y.(2002) J Mol Biology 318: 443-453
- PubMed: 12051850
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(02)00111-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1JI1, 1JI2 - PubMed Abstract:
The X-ray crystal structures of Thermoactinomyces vulgaris R-47 alpha-amylase 1 (TVAI) and alpha-amylase 2 (TVAII) have been determined at 1.6 A and 2.3 A resolution, respectively. The structures of TVAI and TVAII have been refined, R-factor of 0.182 (R(free)=0.206) and 0.179 (0.224), respectively, with good chemical geometries. Both TVAI and TVAII have four domains, N, A, B and C, and all very similar in structure. However, there are some differences in the structures between them. Domain N of TVAI interacts strongly with domains A and B, giving a spherical shape structure to the enzyme, while domain N of TVAII is isolated from the other domains, which leads to the formation of a dimer. TVAI has three bound Ca ions, whereas TVAII has only one. TVAI has eight extra loops compared to TVAII, while TVAII has two extra loops compared to TVAI. TVAI can hydrolyze substrates more efficiently than TVAII with a high molecular mass such as starch, while TVAII is much more active against cyclodextrins than TVAI and other alpha-amylases. A structural comparison of the active sites has clearly revealed this difference in substrate specificity.
- Department of Biotechnology and Life Science, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, 2-24-16 Naka-cho, Koganei, Tokyo 184-8588, Japan. kamitori@cc.tuat.ac.jp
Organizational Affiliation: